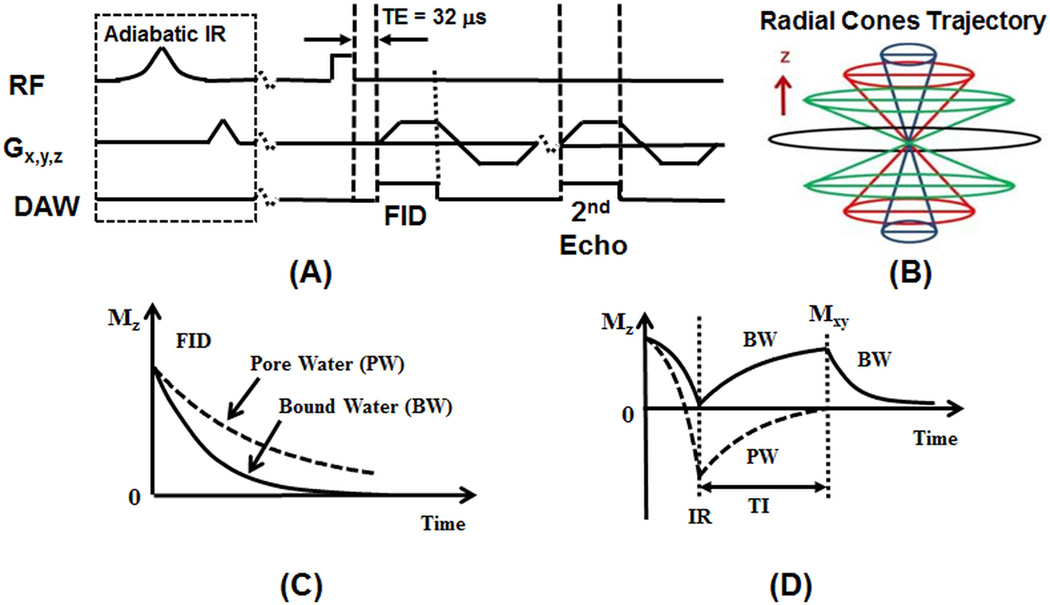
Figure 1.
The 3D UTE and IR-UTE sequences (A), and radial trajectories with conical view ordering in k-space (B), as well as the contrast mechanisms for UTE imaging of total water (B) and IR-UTE imaging of bound water (D). The 3D UTE sequence employs a short rectangular pulse for signal excitation followed by 3D radial ramp sampling with a minimal nominal TE of 32 µs, allowing detection of both bound and pore water (C). The 3D IR-UTE sequence employs an adiabatic inversion pulse to invert and null the pore water magnetization. The bound water magnetization is not inverted and is detected by a subsequent UTE data acquisition (D).