Figure 3.
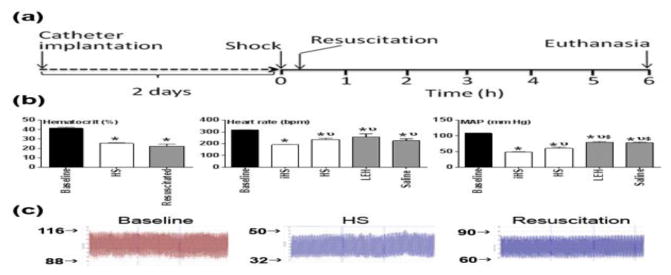
Experimental design. (a) Hemorrhagic shock was induced by withdrawing 45% of blood through an indwelling femoral artery catheter. The catheter surgery was performed at least 2 days before the shock study. The hemorrhaged rats were resuscitated with saline or LEH in volumes equal to the shed blood. The untreated hemorrhaged rats (HS group) received no treatment. The control group consisted of normal rats subjected to catheter implantation, but no hemorrhage or resuscitation was provided. At 6 h, the rats were euthanized and plasma samples were collected for evaluations described in this article. (b) Hemodynamic parameters (hematocrit, heart rate, and mean arterial pressure) recorded at baseline, immediately after blood withdrawal (iHS), after 6 h of shock (HS), and saline or LEH resuscitation (c) A representative trace of raw blood pressure readings. p < 0.05 vs. Ctrl*, iHSν, and HS$
