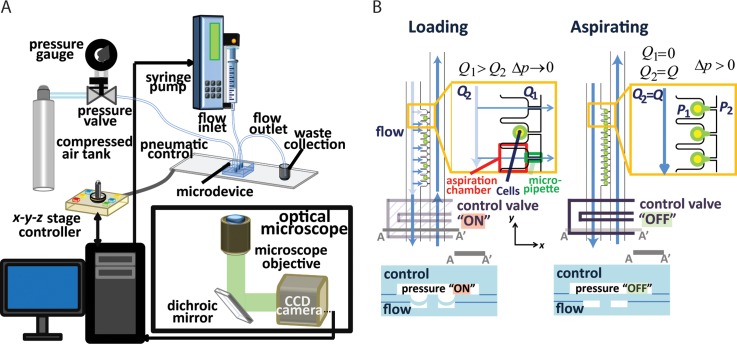
FIG. 2.
Operation principle of the microfluidic micropipette aspiration device. (a) Experimental setup for device operation. (b) Schematic of trapping (left) and aspiration (right) of cells using the control valves. When the control valves are on (depressed PDMS membrane), the pressure restricts the main microfluidic channel and increases flow into the micropipette channels (Q1 > Q2). When all the cells are trapped, the control valves are turned off to generate pressure differences across the micropipettes to begin cell aspiration.