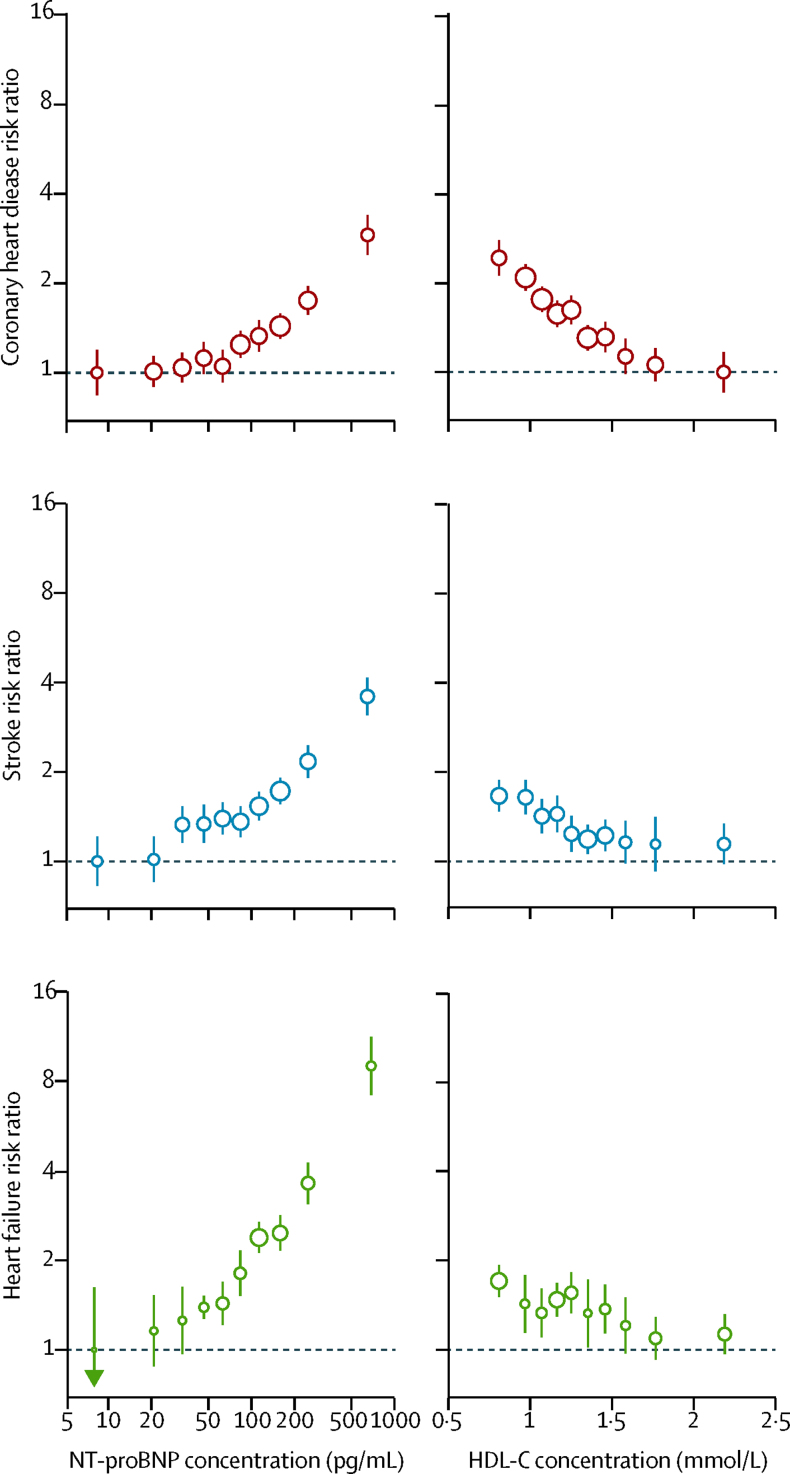
Figure 1.
Associations of NT-proBNP and HDL-C concentrations with first-onset coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart failure
Risk ratios adjusted for age, smoking status, history of diabetes, systolic blood pressure, and total cholesterol and HDL-C concentration (HDL-C concentration only for NT-proBNP concentration analysis) and stratified by sex. Analyses involved 4716 coronary heart disease outcomes (from 34 cohorts), 3768 stroke outcomes (from 30 cohorts), and 2021 heart failure outcomes (from 16 cohorts). The size of the circles is proportional to the inverse of the variance of the respective estimate. Error bars are 95% CIs, estimated from floated variances. HDL-C=HDL cholesterol. NT-proBNP=N-terminal-pro-B-type natriuretic peptide.