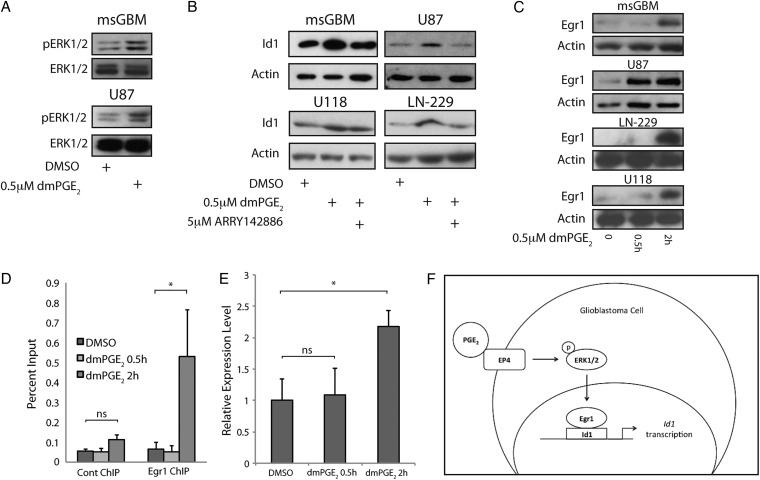
Fig. 3.
MAPK signaling is required for PGE2-mediated induction of Id1 in glioblastoma (GBM) cells. (A) ERK1/2 phosphorylation was induced in mouse primary GBM cells (upper panel) and human U87 cells (bottom panel) in response to 0.5 hour treatment with 0.5 µM dmPGE2. (B) Cotreatment with 5 µM ARRY-142886, a MEK inhibitor, effectively blocked dmPGE2-mediated induction of Id1 at 24 hours in mouse primary GBM cells and U87 cells, and at 4 hours in LN-229 and U118 cells. (C) Expression of the transcription factor Egr1 increased in murine GBM cells and human U87, LN-229, or U118 cells in response to 0.5 µM dmPGE2 treatment. (D) Chromatin IP was performed on mouse GBM primary cultures, revealing specific recruitment of Egr1 to a conserved Egr1 binding site within the Id1 promoter 2 hours after 0.5 µM dmPGE2 treatment. Quantitative PCR was used to calculate the percent input for each chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) sample. Error bars represent mean ± SEM (n = 3). *, P < .05. (E) Egr1 binding coincided with an increase in Id1 mRNA following treatment with dmPGE2 for 2 hours, as measured by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent mean ± SEM (n = 3). *, P < .05. (F) A general schematic of the signal transduction pathway by which PGE2 induces Id1 transcription.