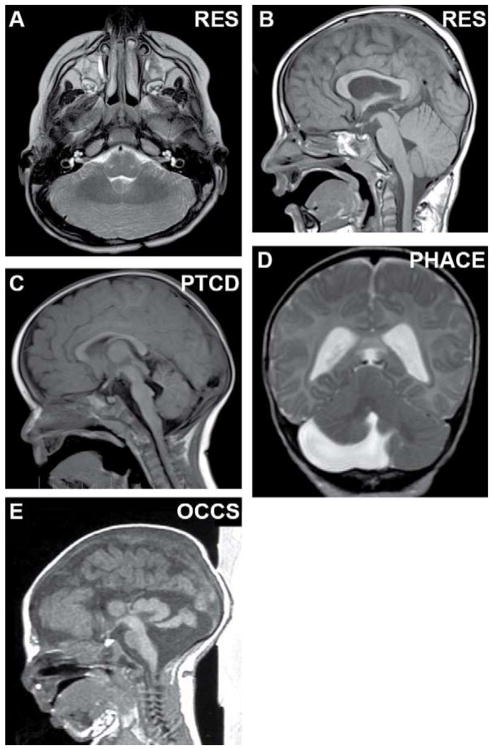
Fig. 3.
Cerebellar malformations without known genetic causes. (A, B) Axial and sagittal views of rhombencephalosynapsis with absent vermis, fusion of the hemispheres, and lack of vermis morphology on sagittal view. (C) Sagittal view of pontine tegmental cap dysplasia with dorsal “cap”, absence of the ventral pons and mild vermis hypoplasia. (D) Coronal view of unilateral cerebellar hypoplasia in PHACE syndrome (Posterior fossa malformations, Hemangioma, Arterial anomalies, Cardiac defects and Eye anomalies). (E) Sagittal view of massively enlarged tectum and vermis hypoplasia with preserved pons in oculocerebrocutaneous syndrome. (B, C) Adapted with permission from Doherty et al. [12].