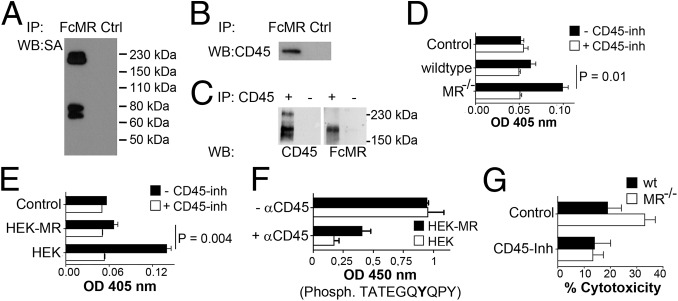
Fig. 2.
Interaction of the MR with CD45 impairs its phosphatase activity and is responsible for reduced cytotoxic activity. (A) FcMR or isotype controls (Ctrl) were added to the lysate of surface biotinylated DesTCR T cells and immunoprecipitated (IP). Eluates were analyzed by Western blot (WB) using HRP-conjugated streptavidin (SA). (B) Identical to A using a CD45-specific antibody. (C) Lysates of wild-type splenocytes were incubated with or without a CD45-specific antibody and immunoprecipitated. Eluates were analyzed by Western blot using FcMR or a CD45-specific antibody. (D) CD45 from lysates of DesTCR T cells that were incubated with wild-type or MR−/− BM-DCs was immunoprecipitated, and 2 mM 4-nitrophenyl phosphate was added in the presence or absence of 1 μM CD45 inhibitor (Inh) N-(9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydro-phenanthren-2-yl)-2,2-dimethyl-propionamide. Dephosphorylation of 4-NPP was monitored by colorimetry at 405 nm. Samples without αCD45 were used as controls. (E) Identical to D using HEK293T (HEK) or MR-expressing HEK293T (HEK-MR) cells. (F) Dephosphorylation of TATEGQ-pY-QPQ by immunoprecipitated CD45 after incubation with HEK or HEK-MR cells. Phosph., phosphorylated. (G) Cytotoxic activity of DesTCR T cells activated by wt or MR−/− BM-DCs in the presence or absence of 40 nM SF1670. Bar graphs depict statistical analysis (mean ± SEM) of replicates from three independent experiments. OD, optical density.