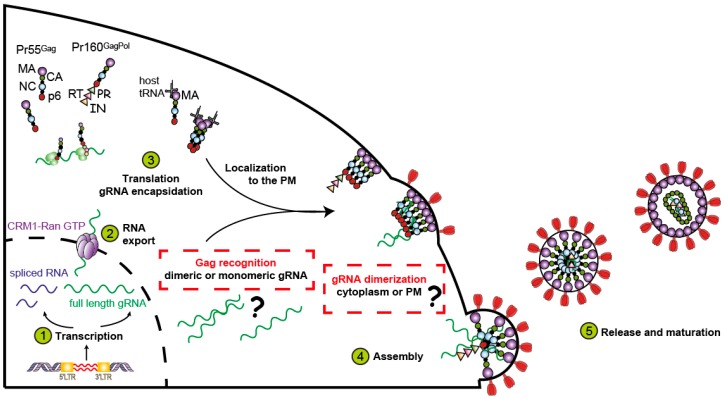
Figure 1.
The late phase of retroviral cycle highlighting the dimerization event and the Gag–RNA complex formation. Full-length genomic RNA (gRNA) as well as singly and multi-spliced viral RNAs are produced by the host cell machinery and exported into the cytoplasm. Two copies of genomic RNA (gRNA) are encapsidated inside the newly synthesized viral particle as a dimer. The interaction of Gag with the gRNA in the cytoplasm ensures its specific encapsidation. Targeting of the Gag–RNA complex to the plasma membrane (PM) is promoted by host transfer RNA (tRNA) binding to the Gag matrix (MA) domain. Since the spatio-temporal parameters of these related events remain unclear, this figure depicts the different possibilities. CA: capsid; NC: nucleocapsid; RT: reverse transcriptase; PR: protease; IN: integrase; CRM1: Chromosomal Maintenance 1; LTR: long terminal repeat.