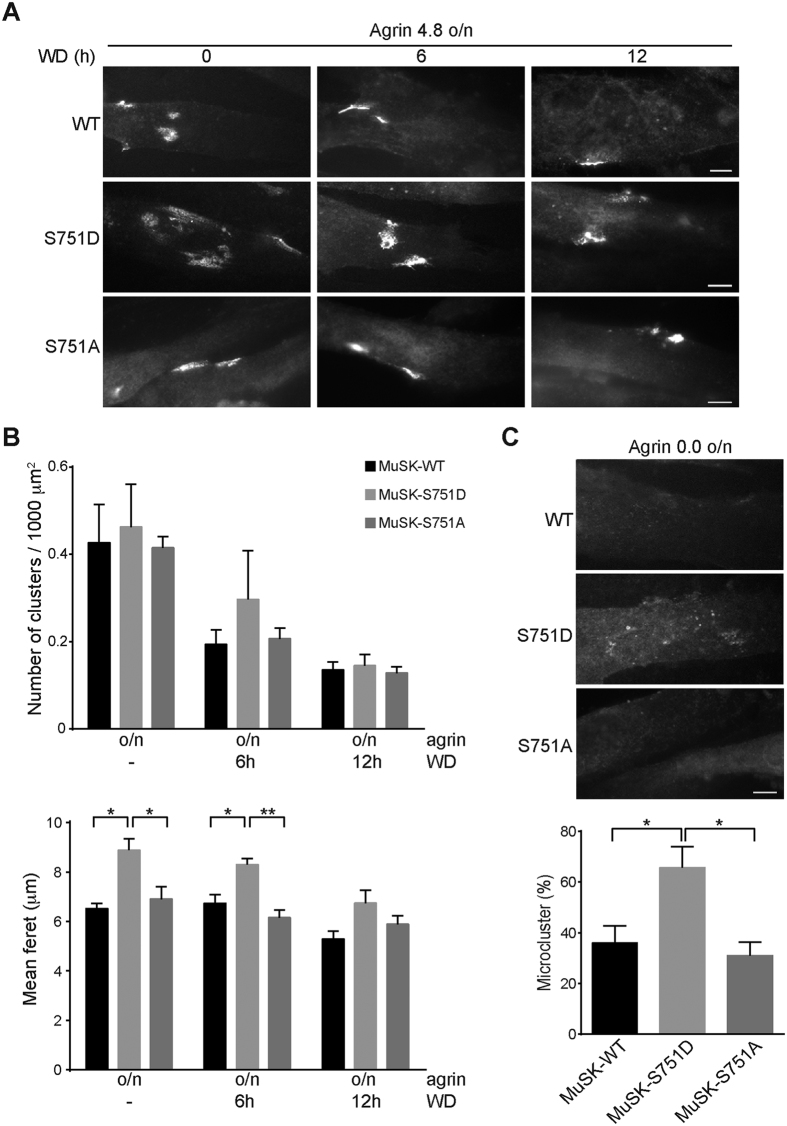
Figure 6. A MuSK S751 phosphomimetic mutant increases the size of AChR clusters but does not increase the number of AChRs.
(A) MuSK−/− muscle cells expressing MuSK wild-type and S751 mutant proteins were differentiated and stimulated with agrin for 16 h (overnight) to induce AChR cluster formation. To measure AChR cluster stability, agrin was removed and the cells were maintained in agrin-free medium for indicated times. Representative images of clusters stained with Alexa 594-conjugated α-BGT are shown. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) The number of AChR clusters normalized to myotube area (Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple comparison test, mean ± S.E.M., n = 4 with > 75 myotubes in total for each treatment) and the mean feret of clusters (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test, mean ± S.E.M., *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, n ≥ 100 from four different experiments) were quantified using ImageJ. Note that AChR clusters are significantly bigger in cells expressing MuSK-S751D after agrin stimulation and after 6 h of agrin withdrawal. (C) Graph showing the percentage of microclusters per myotube. MuSK-S751D expressing cells form more microclusters compared to cells expressing MuSK-S751 A (p = 0.0270) and MuSK-WT (p = 0.0382). Values are presented as the mean ± S.E.M. (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test, n = 3 with > 100 myotubes in total for each cell line). WD, withdrawal; o/n, overnight; WT, wild-type.