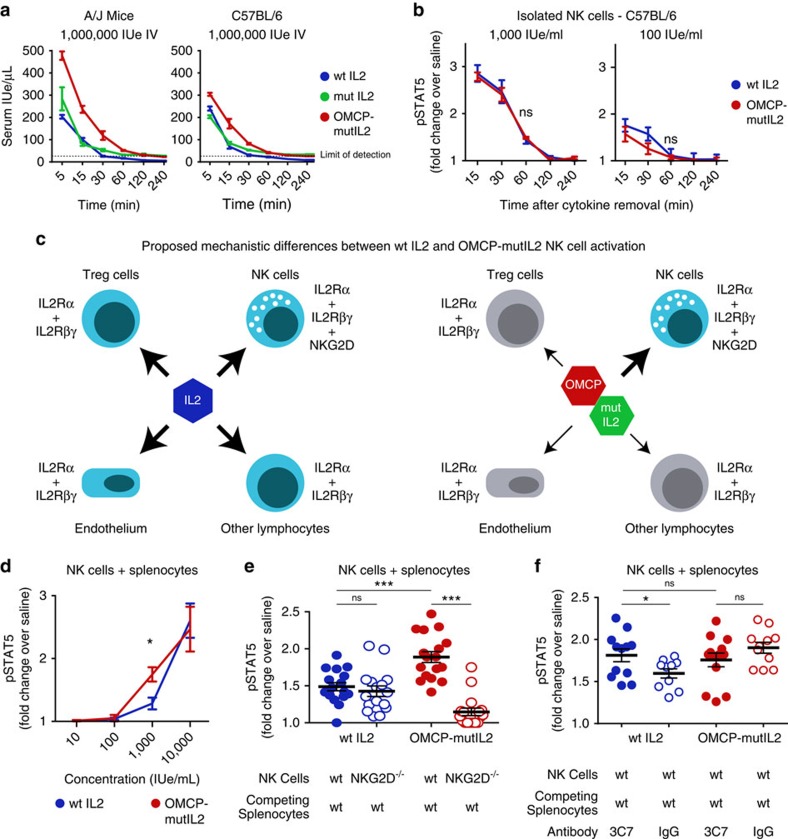
Figure 7. Mechanism of OMCP-mutIL-2 Competition with Stromal Cells.
(a) Serum levels of fluorochrome-labelled cytokine or fusion protein after injection of 1 × 106 IUe (i.v.) determined fluoroscopically according to a standard curve. (b) Decay in STAT5 phosphorylation after a 15-minute stimulation by 1,000 IUeml−1 (left) or 100 IUe ml−1 (right) of IL-2 or OMCP-mutIL-2 as determined flow cytometrically. Comparison performed by multiple unpaired t-tests at each individual time point. (c) Proposed model of competition between NK cells and stromal cells for IL-2. Width of arrow indicates proposed strength of IL-2 signaling. (d) Dose response in STAT5 phosphorylation of C57BL/6 NK cells in the presence of other splenocytes by wtIL-2 and OMCP-mutIL-2 as determined by flow cytometric staining. Comparison performed by multiple unpaired t-tests at each individual cytokine concentration. (e) STAT5 phosphorylation of wild-type or NKG2D−/− NK cells by wtIL-2 and OMCP-mutIL-2 in the presence of competing splenocytes. (f) STAT5 phosphorylation, as measured by fold change over saline-treated controls, of wild-type NK cells in the presence of competing splenocytes treated with saturating concentrations of rat anti-mouse CD25 (clone 3C7) or rat IgG isotype control. Comparison performed by unpaired t-test between groups as indicated by the lines above the graphs. ns P>0.05; *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; blue=wtIL-2, red=OMCP-mutIL-2, green=mutIL-2.