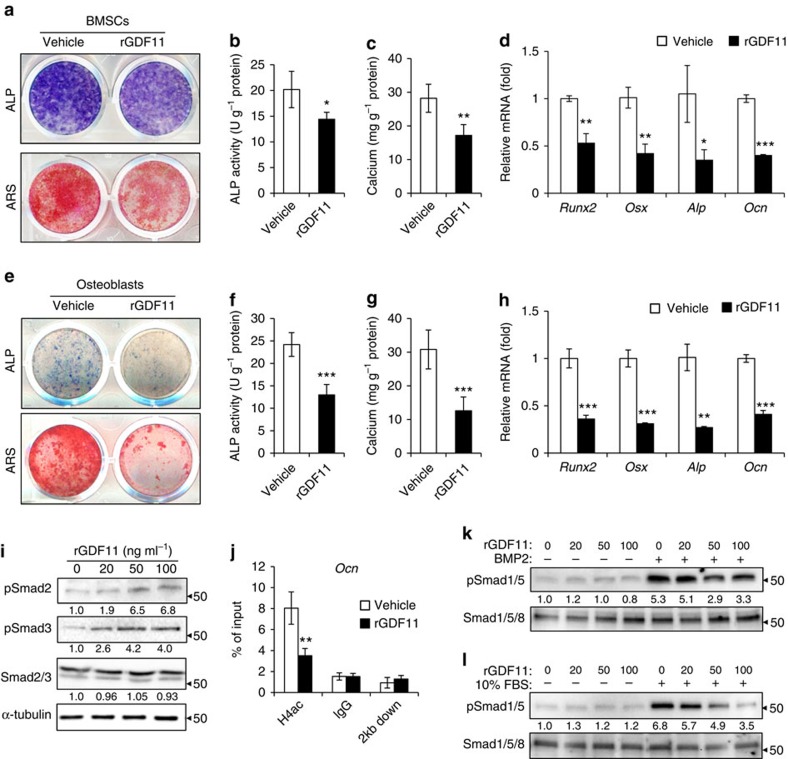
Figure 5. GDF11 inhibits osteoblast differentiation.
(a) Representative images of ALP staining and Alizarin Red S (ARS) staining of BMSCs. (b,c) Quantitative analyses of the ALP activity and calcium mineralization in BMSCs. Results are shown as mean±s.d.; n=5; *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 by t test. (d) Quantitative RT-PCR revealed reduced messenger RNA expression of Runx2, Osx, Alp and Ocn in rGDF11 treated BMSCs. Results are shown as mean±s.d.; n=5; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 by t test. (e) Representative images of ALP and ARS staining of primary calvarial osteoblasts. (f,g) Quantitative analyses of the ALP activity and calcium mineralization in osteoblasts. Results are shown as mean±s.d.; n=5; ***P<0.001 by t test. (h) Quantitative RT-PCR demonstrated that rGDF11 inhibited messenger RNA expression of Runx2, Osx, Alp and Ocn in osteoblasts. n=3. Results are shown as mean±s.d.; n=5; **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 by t test. (i) Western blot indicated that rGDF11 stimulated the phosphorylation of Smad2/3 in osteoblasts. (j) ChIP assay revealed that rGDF11 reduced the abundance of acetylated histone H4 (H4ac) on the promoter of Ocn. Results are shown as mean±s.d.; n=3; **P<0.01 by t test. (k,l) Western blot analysis of pSmad1/5. The presence of rGDF11 attenuated BMP2 or foetal bovine serum induced phosphorylation of Smad1/5. Osteoblasts were starved overnight and then treated for 30 min.