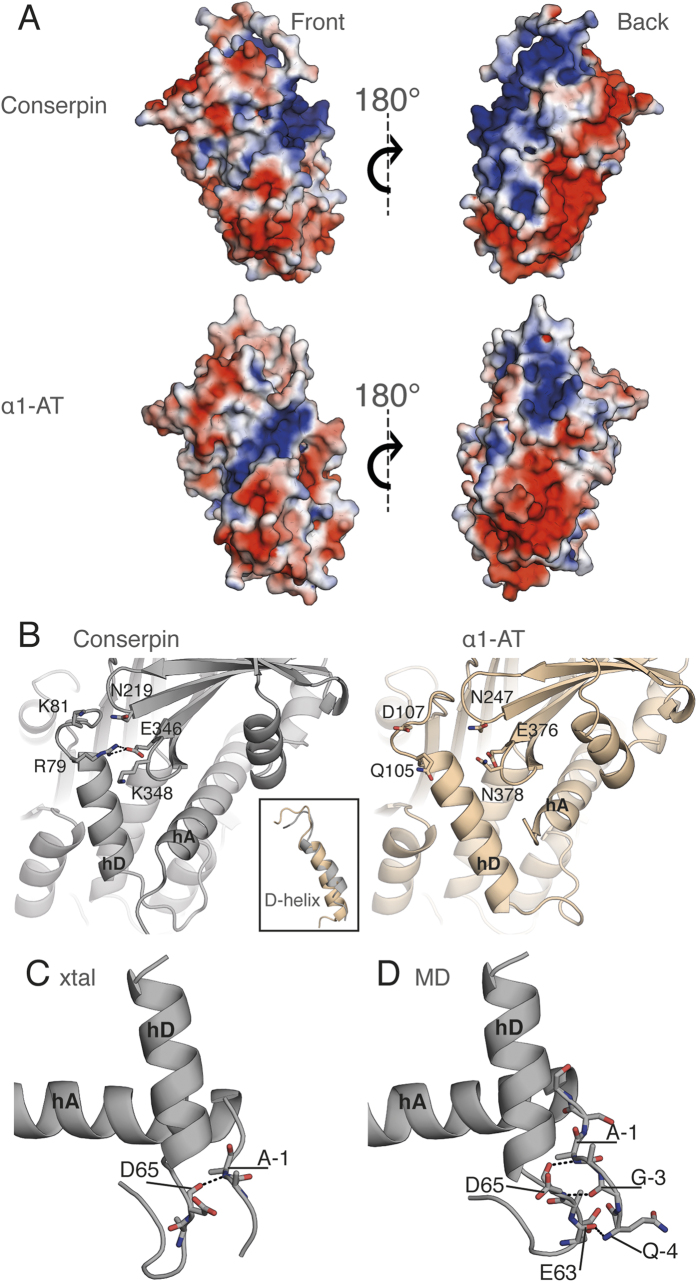
Figure 2. Structural analysis reveals alterations of the electrostatic surface and stabilization of the D-helix in conserpin.
(A) The electrostatic potential surface of conserpin and α1-AT models (blue = +ve, red = −ve), in the same orientation as Fig. 1A (front) and a 180° rotation reveals an overall increase in positive charge on the back face of conserpin. (B) The introduced salt bridge in hD of conserpin with residues Q105R79 and E376346. There is no comparable interaction present in α1-AT. Inset shows the shortened D-helix in conserpin. (C) H-bonding between A-1 of the extended N-terminus and D65 of hD, as seen in the conserpin crystal structure. (D) Persistent hydrogen bonding between Q-4, G-3 and A-1 of the extended N-terminus and E63 and D65 of hD in conserpin as seen in MD simulation.