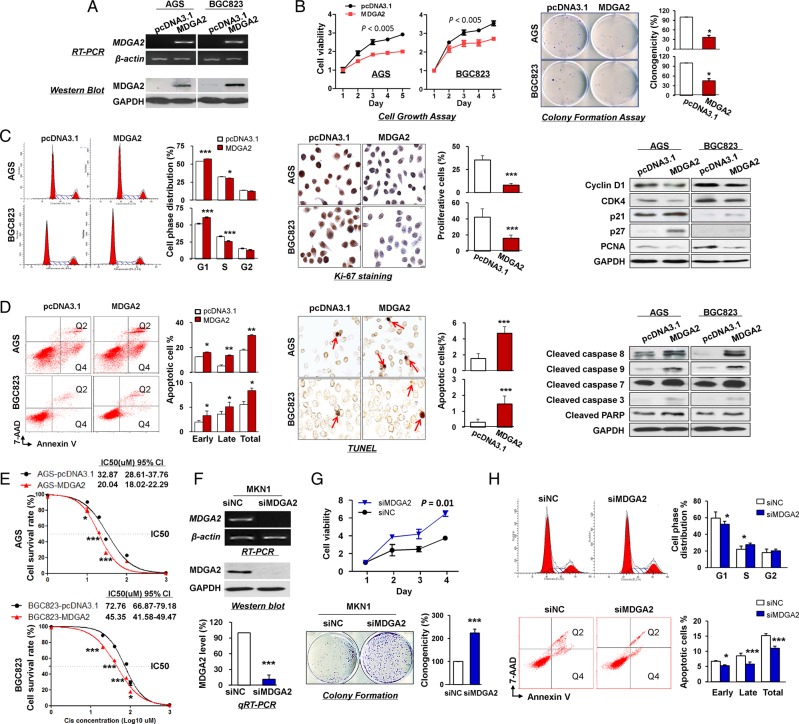
Figure 3.
In vitro gain- and loss-of-function assays on MDGA2. (A) Ectopic expression of MDGA2 in AGS and BGC823 cells at mRNA and protein levels was confirmed by reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) and western blot analysis. (B) MDGA2 significantly inhibited cell viability and colony formation ability. (C) MDGA2 caused cell cycle arrest at G1–S transition, as indicated by flow cytometry. Reduced cell proliferation by MDGA2 was further shown by Ki-67 staining (magnification ×400) and altered cell cycle-related protein expression by western blot analysis. (D) Cell apoptosis by flow cytometry analysis after annexin V-APC and 7-aminoactinomycin (7-AAD) double staining. Q2 shows the late apoptotic cells and Q4 shows the early apoptotic cells. Cell apoptosis was confirmed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-digoxigenin nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining (magnification ×400) and upregulation of apoptosis-related proteins in MDGA2-expressing cells was confirmed by western blot analysis. (E) Growth inhibitory effect of cisplatin on MDGA2-overexpressing and control vector-transfected AGS and BGC823 cells. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay after 48 h treatment with cisplatin. Data are mean±SD from three independent experiments. (F) Knockdown of MDGA2 in MKN1 cells by short interference RNA (siRNA) transfection was confirmed by RT-PCR, qRT-PCR and western blot analysis. (G) Knockdown of MDGA2 significantly increased cell viability of MKN1 cells, promoted colony formation and (H) promoted cell cycle progression, but reduced cell apoptosis as indicated by flow cytometry. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.