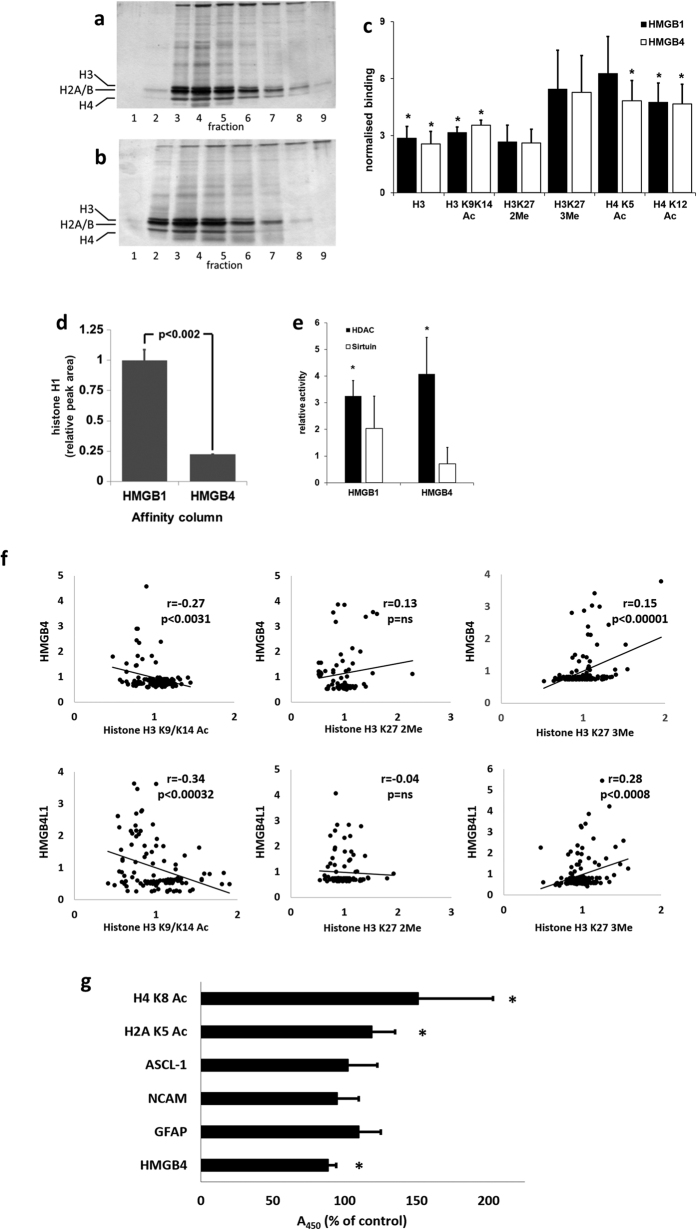
Figure 3. Interactions of HMGB4 and HMGB4L1 with histones.
(a,b) Binding of C6 -cell nuclear proteins to HMGB-protein affinity columns. Proteins in elution fractions were analyzed with silver stained SDS-PAGE. The bands, representing core histones, are indicted with marks on the left. a = HMGB1 –affinity column, b = HMGB4 –affinity column. (c) Core histones eluted from HMGB-protein affinity columns and histones were quantified with ELISA. Affinity chromatography was done as described above (n ≥ 3, *p < 0.05, ±SD; Ac = acetylated, 2Me = di-methylated, 3Me = tri-methylated (lysine)). (d) HMGB1 and HMGB4 differ in their histone H1 binding capacity. Affinity chromatography was done as described above and eluted proteins were analyzed with histone H1 ELISA. Elution peak areas were quantified (n = 3, ± SD, *p < 0.002). (e) HDACs bind to HMGB1 and HMGB4. Nuclear proteins were analyzed with affinity chromatography as described above except that eluted fractions from each column were pooled to form a single fraction. Relative HDAC and sirtuin activities in elution fractions were determined (n ≥ 3 in each experiment, ±SD). (f ) Immunofluorescence intensities of modified histone antibody stained HMGB4 or HMGB4L1 overexpressing cells. Rat glioblastoma C6- cells transiently expressing HMGB4-V5 or HMGB4L1-V5 were double-immunostained with anti-acetylated (K9/K14), anti-dimethylated K27 or anti-trimethylated K27 histone H3 antibodies and with anti-V5 antibodies. The correlation blots are shown. (g) Regulation of protein levels in neuronal precursor cells by HMGB4 shRNA. Human neuronal precursor NTERA-2 cl. D1 cells stably overexpressing HMGB4 shRNA or control nonspecific shRNA were analyzed in cell ELISA. Absorbance values of HMGB4 shRNA expressing cells were normalized to values of control shRNA expressing cells (n ≥ 3, ± SD, *p < 0.03). H2A K5 Ac = histone H2A acetylated lysine 5, H4 K8 Ac = histone H4 acetylated lysine 8.