Figure 4. HEK 293T -cells overexpressing HMGB4-EGFP have increased sensitivity to topoisomerase inhibitors and altered histone variant composition.
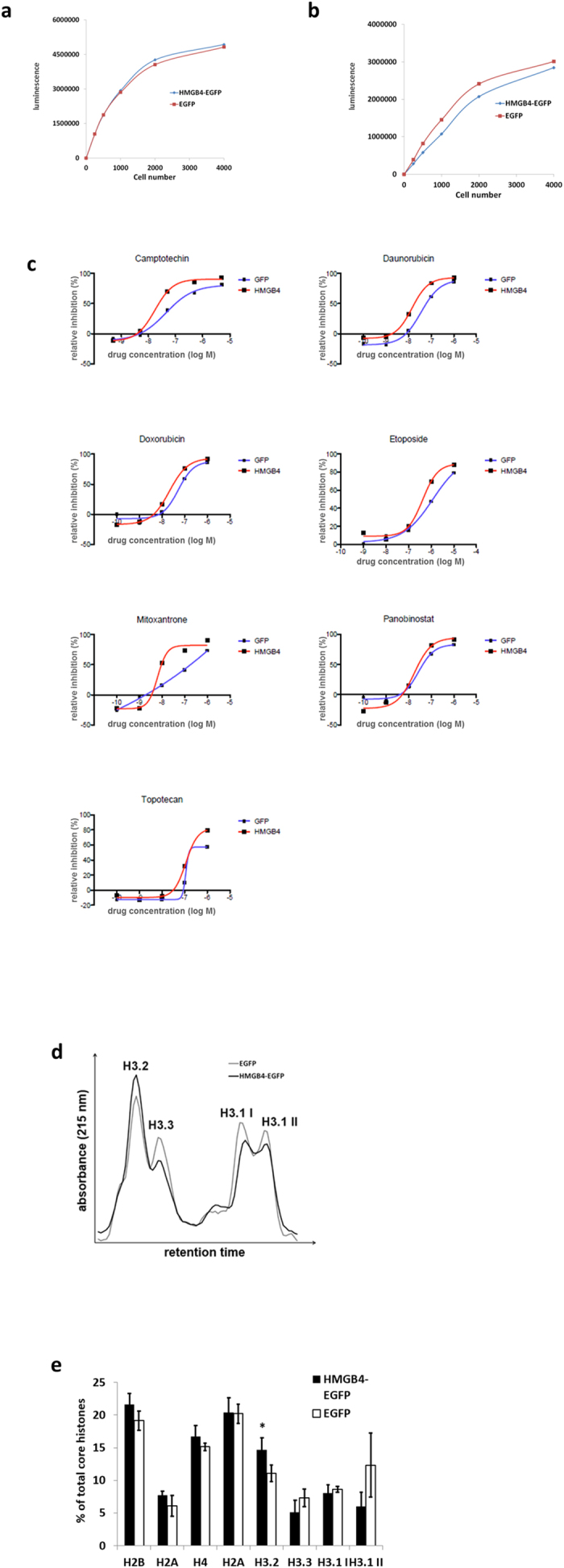
(a) Growth of HEK 293T -cell clones with doxycycline induced HMGB4-EGFP or EGFP -expression. The expression of HMGB4-EGFP or EGFP in cells was induced over one week with doxycycline and viability was measured with CellTiterGlo Luminescent assay reagent via ATP quantification. (b) Growth of stable HEK 293T -cell clones, constantly expressing HMGB4-EGFP or EGFP. Cells were cultured for 72 h and viability was measured as described above. (c) Overexpression of HMGB4 increases cell sensitivity to topoisomerase inhibitors. Cells overexpressing HMGB4-EGFP were more sensitive to topoisomerease inhibitors than control cells expressing EGFP. Figure shows representative curves from two different experiments. (d) Quantification of histone H3 variants of HMGB4-EGFP or EGFP-expressing HEK 293T -cell clones. Histones were isolated from the cells and analyzed with RP-HPLC. Histone peaks were identified according to their relative retention times. Histone H3.1 eluted in two peaks (H3.1 I and H3.1 II). Curves are derived from three EGFP -control cell clone analyses and from three HMGB4-EGFP –cell clone analyses. (e) Maximal core histone peak heights of RP-HPLC (see above) were determined with the UNICORN- software. Peak height sum of core histones was determined as 100% and relative peak heights were calculated. The relative amount of histone H3.2 was elevated in the HMGB4-EGFP -expressing cells when compared to the control cells (n = 3, ±SD, *p < 0.05).
