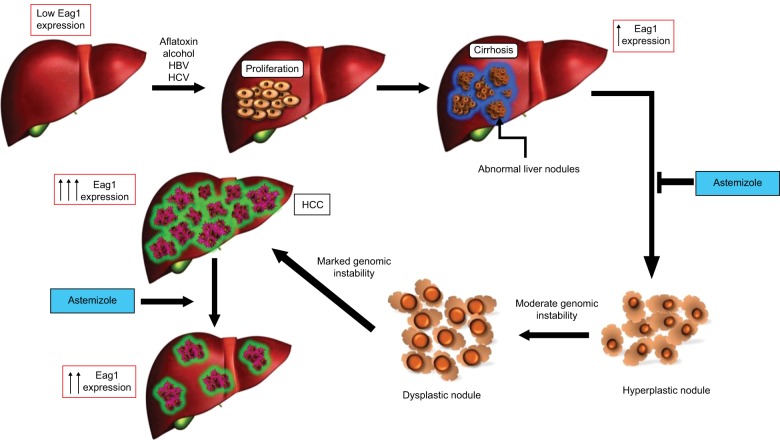
Figure 1.
Eag1 expression in the progression of HCC.
Notes: The principal risk factors for the development of HCC induce serious liver damage, causing necrosis and proliferation in the hepatocyte. This phase is known as chronic liver disease and may continue to liver cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is characterized by the presence of fibrosis; during this process, the connective tissue separates the liver into multiple regeneration nodules, that is, the fibrosis surrounds the nodules completely. The hyperplastic nodules evolve to dysplastic ones and ultimately to HCC. The use of astemizole in the cirrhosis stage may prevent the development of HCC and even produce HCC regression. Eag1 channels have been shown to be expressed at early stages of HCC development.32
Abbreviations: Eag1, ether à-go-go-1; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma.