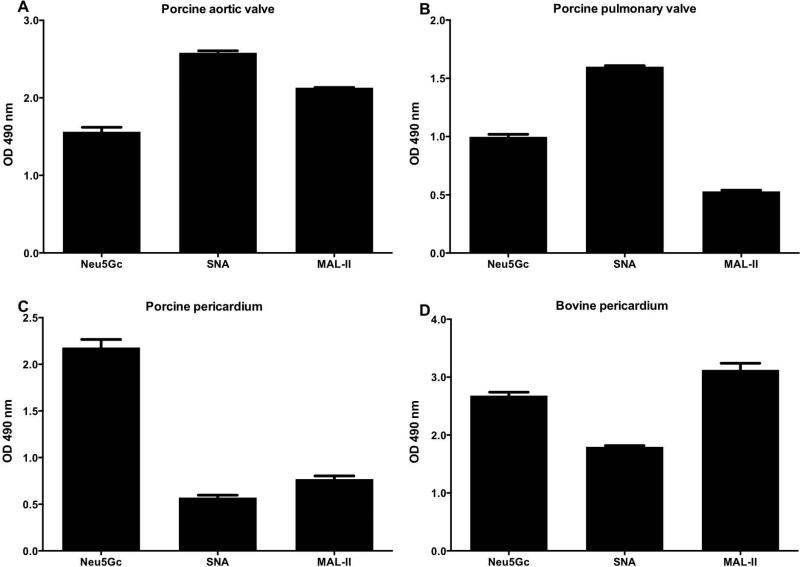
Figure 2.
Characterization of sialic acids in xenogenic cardiac tissues by ELISA. Tissue homogenates of native porcine aortic valve cusp (A), pulmonary valve cusp (B), pericardium (C), and bovine pericardium (D) were coated onto a 96-well plate and analyzed with anti-Neu5Gc IgY (Neu5Gc), biotinylated-SNA lectin or biotinylated-MAL-II lectin (detect α2–6-linked or α2–3-linked sialic-acids, respectively), washed then detected with HRP-anti-chicken IgY or HRP-streptavidin, respectively. All tissue samples express Neu5Gc, with higher levels in pericardium compared to valve cusps (at least two different samples from each tissue were tested, data represent three independent experiments; mean ± SEM).