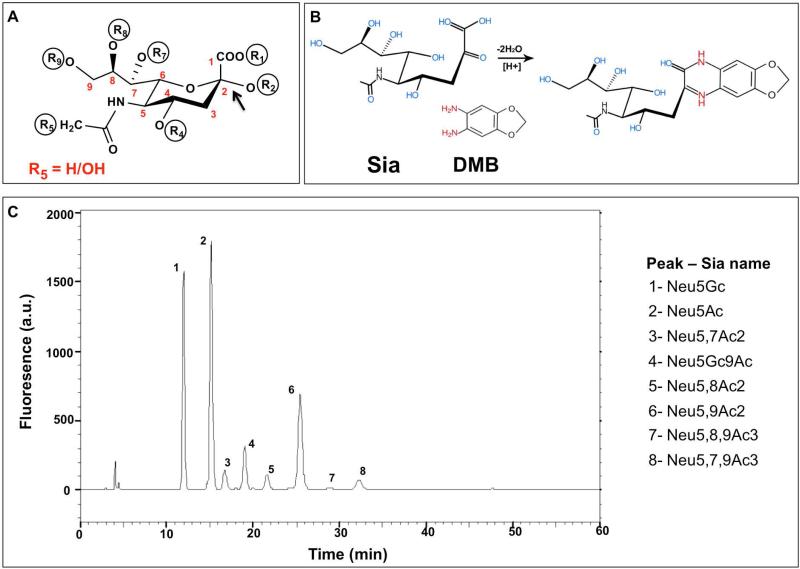
Figure 3.
Sialic acids analysis by DMB-HPLC of Bovine Submaxilary Mucins (BSM). (A) Schematic representation of Sia structure, the backbone carbons are numbered C-1 through C-9. The carboxylate group R1 is negatively charged at neutral pH; Sia is linked to underlying glycans through R2; R5 marks the difference between Neu5Gc (R5=OH) and Neu5Ac (R5=H). Positions R4, R7, R8, R9 can either carry hydroxyl or be modified with O-acetyl group. (B) Sia derivatized with 1,2-diamino-4,5-methylenedioxybenzene (DMB) becomes fluorescent. (C) Sialic acids profile of Bovine Submaxilary Mucins. BSM was hydrolyzed by mild acid hydrolysis (2 M acetic acid that preserves O-Acetylation) then DMB-derivatized and analyzed by reverse-phase HPLC. The analysis shows unique fluorescence peaks for each type of Sia at different retention times, based on hydrophobicity.