Figure 10.
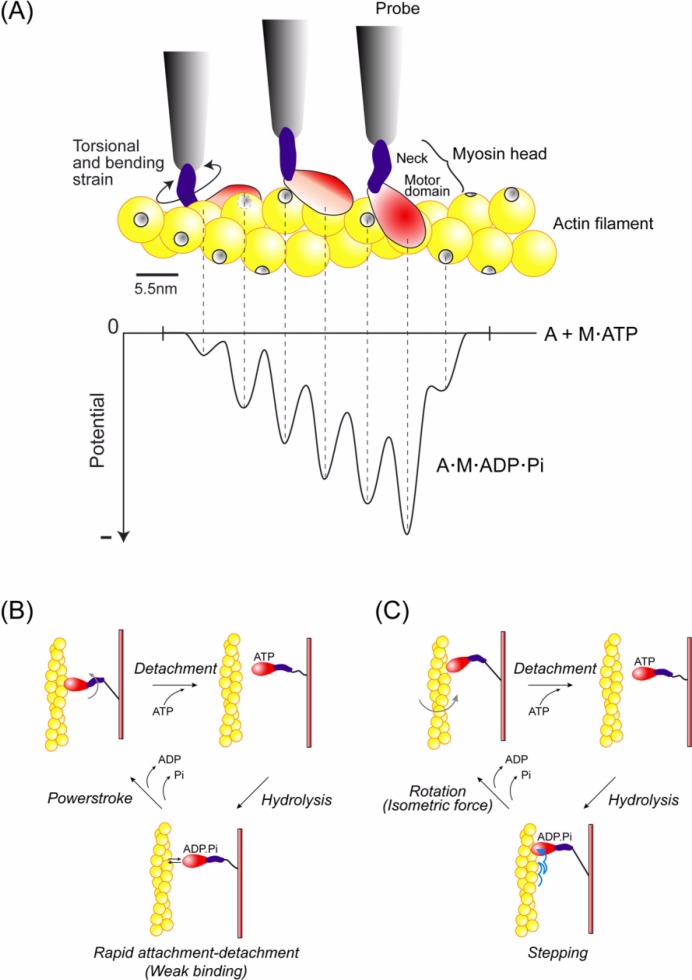
Stepping model based on preferential landing of the myosin head. (A) Potential slope along the actin half helical pitch due to the steric compatibility between the orientations of the binding sites of actin and the myosin head (see text for detail). (B) Mechanochemical coupling for the conventional model. The myosin head undergoes rapid attachment-detachment cycles with actin after ATP hydrolysis and then swings its neck domain (lever arm) to perform a powerstroke, coupled to Pi release77. (C) Mechanochemical coupling for the present model. The myosin head undergoes steps in the forward direction during attachment-detachment cycles. Coupled to Pi release, the head rotates the actin filamen60–64 (see Fig. 11) and stops the step, and isometric force may be generated7,54.