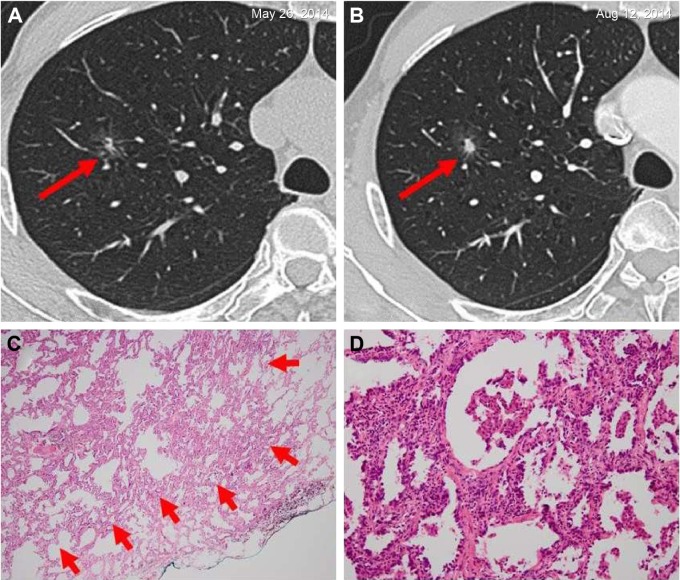
Figure 3.
Invasive adenocarcinoma in a 66-year-old man.
Notes: (A) A solitary ground-glass opacity nodule on the superior lobe of right lung was observed at the time of his medical examination. He had a smoking history of more than 30 years and no individual history of other cancers; his father had colorectal cancer, and his blood tumor markers were negative. The solid composition of the nodule was found to be increased when he was reexamined by HRCT after 3 months (B). Therefore, he decided to undergo surgical resection. Pathological diagnosis indicated that it was an invasive adenocarcinoma. Immunohistochemistry: ALK-V (−), ROS-1 (−). (C) Low magnification (hematoxylin and eosin, original magnification ×40) shows round-to oval-shaped invasive adenocarcinoma (arrows). (D) High magnification of (C) (original magnification ×200).
Abbreviations: ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase; HRCT, high-resolution computed tomography.