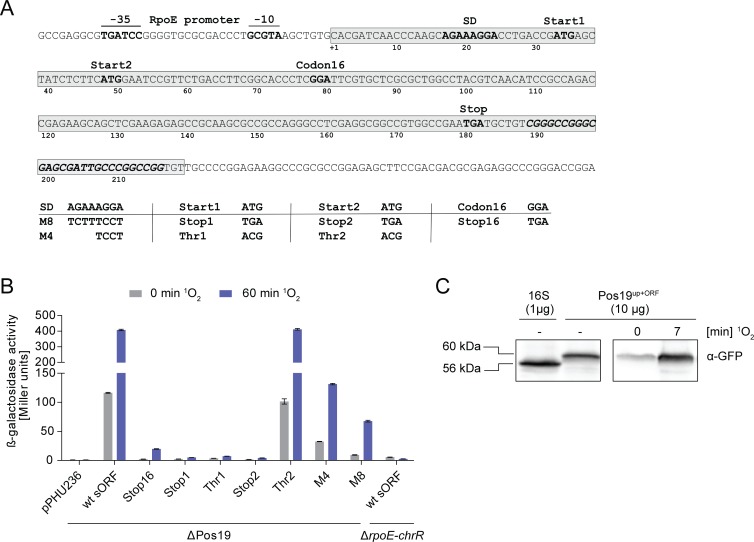
Fig 2. Pos19 is a coding sRNA.
(A) Detailed illustration of the pos19 gene. Relevant features are shown in bold. The -35 and -10 motifs of the RpoE-dependent promoter are marked. The 219 nt long sRNA (shaded in grey) contains two potential ORFs with lengths of 150 (Start1) and 135 nt (Start2). The Rho-independent terminator (italic letters) was predicted by TransTermHP [27] and correlates with the 3’ end mapped by 3’ RACE. The Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence, the two start codons as well as one internal codon (Codon16) were mutated according to the chart below the sequence. (B) In vivo translation of the Pos19-sORF was monitored by translational lacZ fusions. A 300 bp fragment containing the RpoE-dependent promoter and the first 178 bp of the pos19 gene (including codons 1–48) was fused to the promoter-less lacZ gene on reporter plasmid pPHU236. The wild-type (wt) sORF was subsequently mutated as shown in (A). The fusion plasmids and control plasmid pPHU236 were transferred to R. sphaeroides ΔPos19 or strain TF18, which lacks the rpoE-chrR locus. The corresponding strains were subjected to 1O2 stress for 60 min with samples collected at the indicated time points. ß-galactosidase activities were measured from biological triplicates with technical duplicates. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. (C) In vivo translation of the Pos19-sORF was monitored by translational eCFP fusion. The Pos19 peptide, C-terminally fused to eCFP (Pos19up+ORF), was detected with a polyclonal anti-GFP antibody on a Western blot. Cultures were stressed as described for Fig 1 and samples were withdrawn at the indicated time points. The amount of total protein extracts is shown in brackets. Protein from a strain carrying the pBE_eCFP::eCFP with 16S rRNA promoter (16S) was used as control. The size difference between control and Pos19 fusion of around 4 kDa corresponds to molecular weight of the predicted Pos19 peptide.