Figure 3.
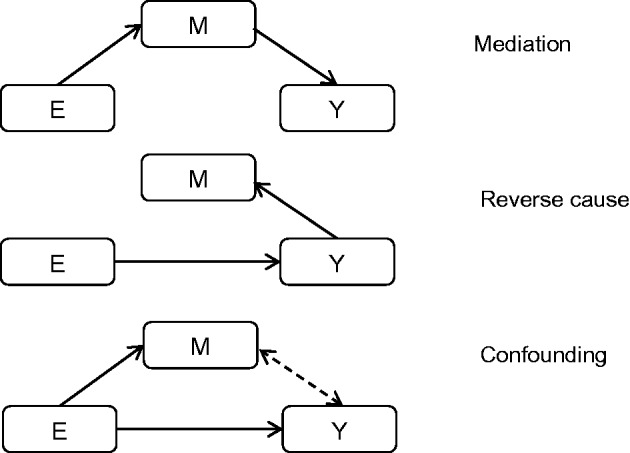
Distinguishing mediation from reverse causation and confounding In a situation of mediation, the effect of the exposure (E) on an outcome (Y) is mediated through an intermediate (M). In a situation of reverse cause, E influences Y which then has an effect on M. In a situation of common cause (confounding), E has an independent effect on both M and Y, so inducing a spurious association between M and Y.
