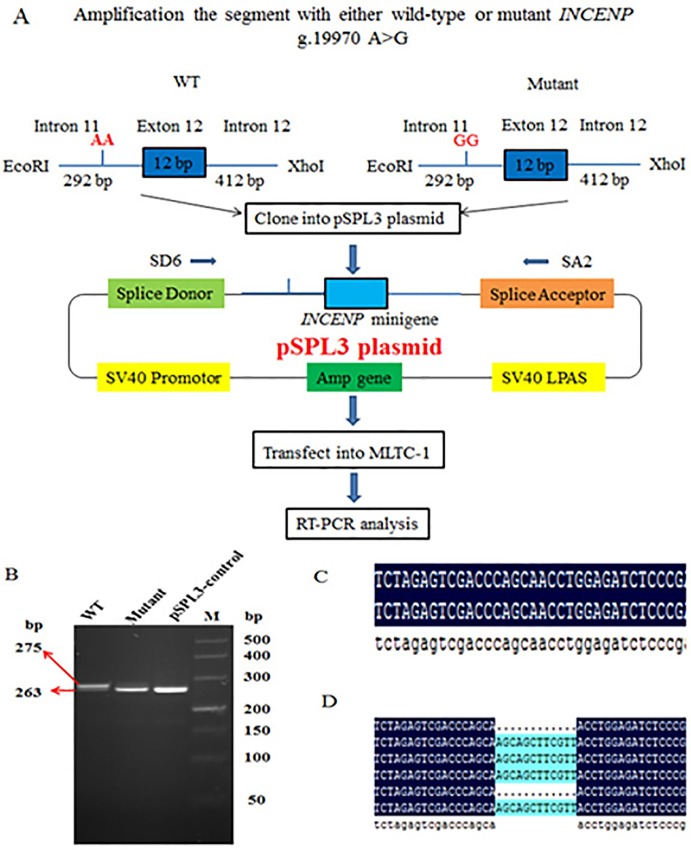
Fig 4. The exon trapping vector pSPL3 used to assay SNP g.19970 A>G function.
(A) The pSPL3 vector contains splice donor (SD) and splice acceptor (SA) sites that operate as exons, and a functional intron, with transcription beginning following the SV40 promoter and ending at the LPAS (late poly (A) signal). Wild-type segment and mutant segment containing 292 bp of intron 11, 12 bp of exon 12, 412 bp of intron 12 and harboring either the A or G alleles were separately cloned into the EcoRI and XhoI cloning sites of the pSPL3 vector. Two minigene expression vectors were transiently transfected into MLTC-1 cells. (B) RT-PCR analysis of the INCENP spliced transcripts on 3% agarose gel. Due to the difference of only 12 bp, the result of electrophoresis is not obvious. (C) cDNA was sequenced and the result shown that mutant and empty pSPL3-control expressed a fragment of 263 bp. (D) Cloning sequencing was implemented to verify the fragment of WT. The result showed that WT obtained 275 bp and 263 bp PCR fragment. The sizes of the fragment (275 bp) corresponded to the amplification exon 12 (12 bp) and pSPL3 control plasmid (263 bp). The size of the fragment (263 bp) corresponded to the pSPL3 control plasmid (263 bp).