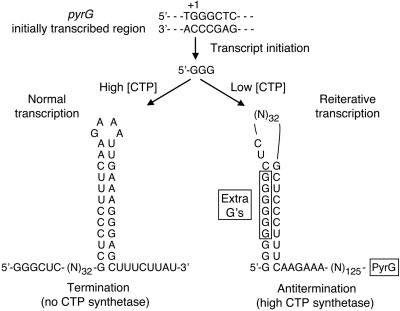
Fig. 3.
Model for CTP-mediated regulation of pyrG expression in B. subtilis. The model shows the effects of CTP concentration on the fate of the pyrG transcript after the first three G residues have been incorporated into the nascent transcript. High CTP concentrations allow normal transcript elongation until intrinsic termination occurs in the pyrG leader region. Low CTP concentrations induce a transcription pause that allows reiterative transcription and the addition of extra G residues, which participate in the formation of an antiterminator hairpin. The extra G residues are boxed. The model shows the insertion of six extra G residues, but as many as 10 extra residues can be added.