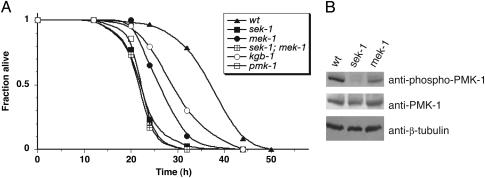
Fig. 1.
Requirement for MEK-1 and SEK-1 in the activation of PMK-1 in C. elegans immunity. (A) Pathogen susceptibility of C. elegans mek-1(ks54), sek-1(km4), mek-1(ks54);sek-1(km4), pmk-1(km25), and kgb-1(km21) mutants. At least 40 L4-stage worms were allowed to feed on lawns of P. aeruginosa strain PA14 and were scored as dead when they no longer responded to touch as described in ref. 32. Representative plots of multiple experiments are shown. All mutant alleles are deletions that are predicted to be null alleles. (B) Immunoblot analysis of PMK-1 activation in young adult whole worm lysates of mek-1(ks54), sek-1(km4), and WT worms by using Abs specific for the doubly phosphorylated activated form of PMK-1 (anti-phospho-p38). Anti-β-tubulin was used as a loading control.