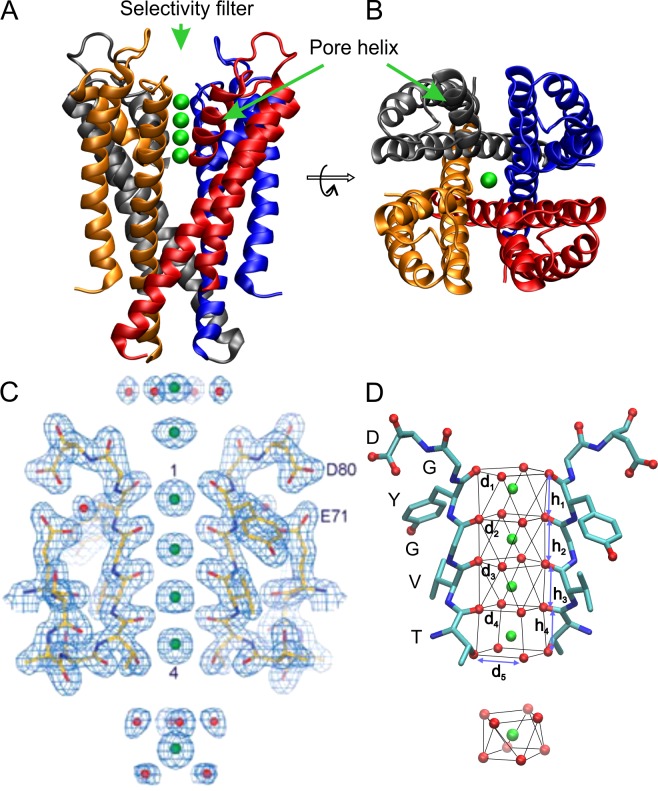
Figure 1.
Structural features of the KcsA channel and K+ coordination structure in the pore. (A and B) Membrane-omitted side and top views of the KcsA K+ channel (PDB ID 1K4C). Each monomer is a two–transmembrane segment peptide position around the pore at the axis of fourfold symmetry forming the K+ selective pore (green spheres). (C) High-resolution electronic density map showing the two diagonal subunits and the orientation of the carbonyl oxygen atoms to coordinate K+ ions. The numbers correspond to the four binding sites determined by the sequence TVGYG. (D) Antiprism and cubic cages forming the selectivity filter binding sites, the distances d1–d5 and heights h1–h4 correspond to the inter-oxygen separations described in Table 1 for several K+ channel structures. A and B were inspired by Doyle et al. (1998), C was modified from Zhou et al. (2001) with permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd., and D was inspired by Chen et al. (2014).