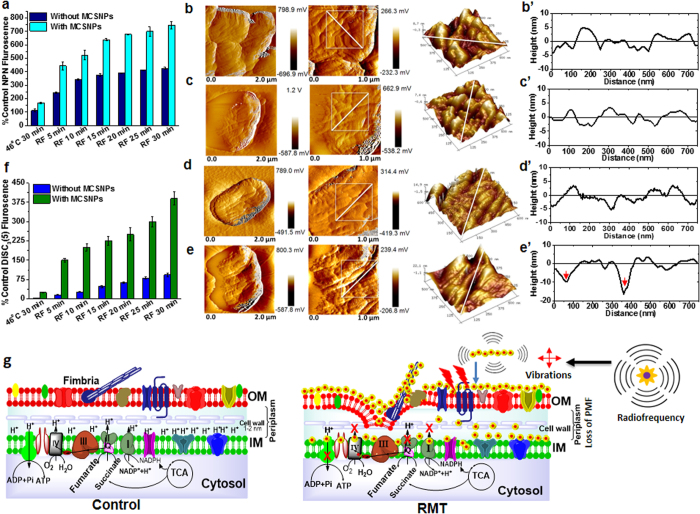
Figure 5. Membrane perturbation of UPEC by RMT.
(a) Outer cell membrane permeability of UPEC by RF and RMT treatments. (b–e’) AFM amplitude mode images of UPEC cell surfaces after treatment at various conditions: (b–e) cell morphology and (b’–e’) outer membrane topography analyses of UPEC incubated at 46 °C without MSCNPs (b,b’), and with MCSNPs (c,c’), UPEC treated with RF at 46 °C without MCSNPs (d,d’), and with MCSNPs at 46 °C (RMT, e,e’). Note that carter-type pits with 10–17 nm depths towards the inner membranes were observed after RMT treatment (e’). (f) Inner membrane (IM) potential of UPEC after RF or RMT treatment at 46 °C. (g) Schematic diagrams showing the UPEC membrane and membrane associated electron transport chain in control cells (left) and cells after RMT treatment (right). Outer membranes were damaged and crater-like pits were formed by ROS, heat, and mechanical vibration from NPs after RF application. Consequently, loss of inner membrane potential and dysfunction of membrane associated complexes followed. Eventually, these factors induce bacterial cell death.