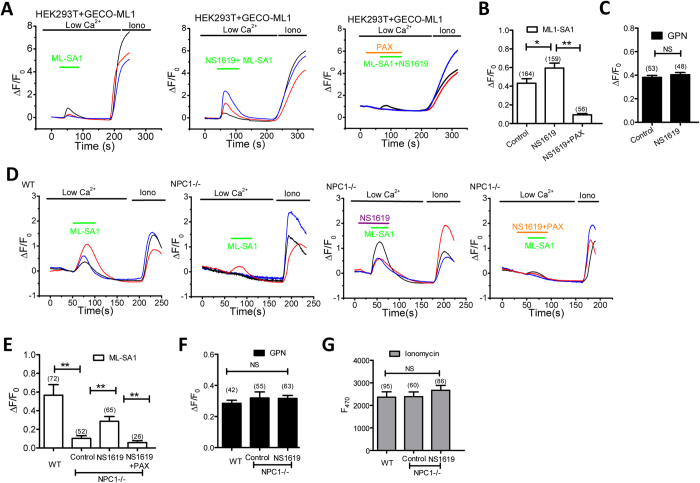
Figure 3. Activation of BK by NS1619 facilitates ML1-mediated Ca2+ release.
(A,B) NS1619 (15 μM) treatment increased ML-SA1 (10 μM)-mediated GECO-TRPML1 response, which was inhibited by co-applying Paxilline (PAX, 3 μM) in HEK293T cells. (C) NS1619 (15 μM) treatment did not alter GECO-TRPML1 response to GPN (200 μM), suggesting lysosomal Ca2+ content was not affected. (D,E) NPC1 human fibroblasts exhibited impaired GECO-TRPML1 response to ML-SA1 (10 μM). NS1619 (15 μM) treatment increased GECO-TRPML1 response to ML-SA1, and this was inhibited by co-applying Paxilline (PAX, 3 μM). (F) GECO-TRPML1 responses to GPN (200 μM) was not altered by NS1619 (15 μM) in NPC1 cells, suggesting that NS1619 does not change lysosomal Ca2+ content. (G) GECO-TRPML1 responses to Ionomycin (1 μM) were not altered, indicating a similar level of GECO-TRPML1 expression.