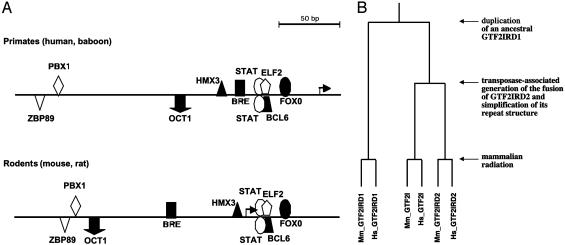
Fig. 4.
Promoter organization of GTF2IRD2 genes and their evolutionary relationship with other members of the GTF2I family. (A) Regulatory elements that can contribute to basal and tissue-specific transcription of primate and rodent GTF2IRD2 genes. The diagram shows the average relative distances calculated either for human and baboon or mouse and rat sequences. Arrow indicates transcription start site. BCL6, POZ/zinc finger protein, transcriptional repressor; BRE, TFIIB recognition element; ELF2, Ets-family member ELF-2/NERF1a; FOXO, Fkh domain factor FKHRL1; HMX3, H6 homeodomain HMX3/Nkx5.1; OCT1, octamer-binding factor 1; PBX1, homeodomain factor Pbx1; STAT, signal transducers and activators of transcription; ZBP89, zinc finger transcription factor ZBP-89. (B) Hypothetic phylogenetic tree of the GTF2I-related genes. The evolutionary distances between sequences are not drawn to scale.