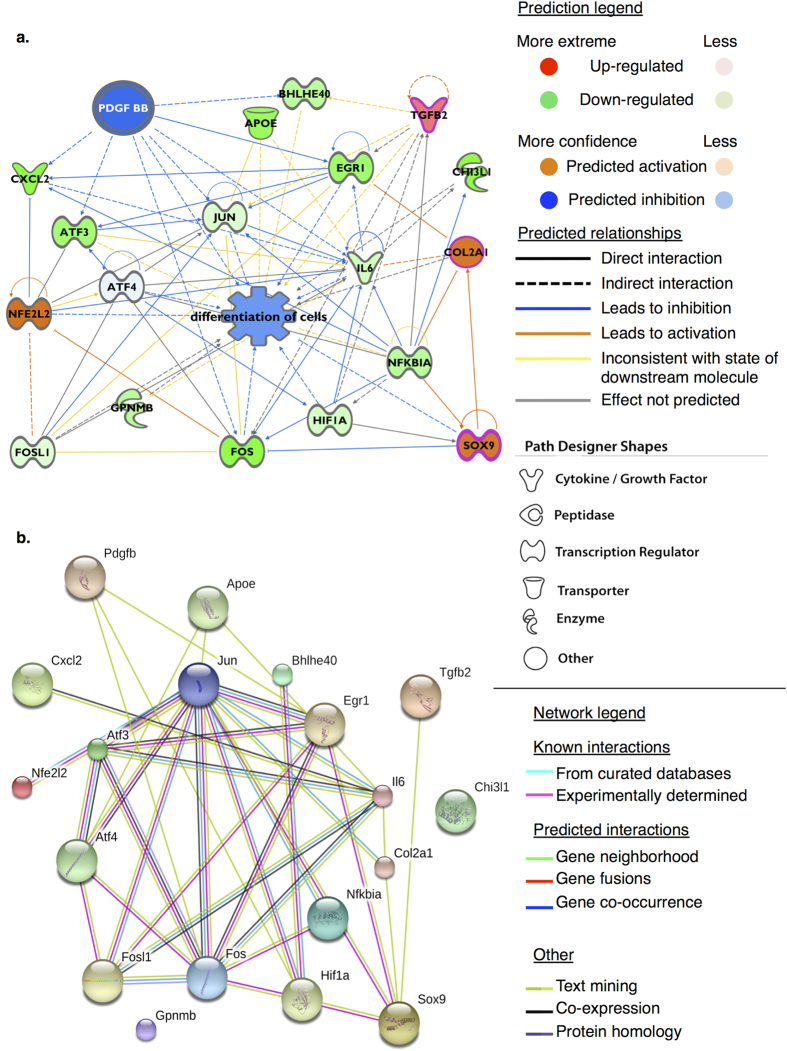
Figure 6.
(a) Hypothetical mechanistic network derived from predicted upstream regulators for genes found to be differentially expression in chondrocytes in transition from monolayer to alginate bead cultures (redifferentiation). Genes showing lower expression in monolayer relative to alginate beads (Hif1a, Nfe2l2, Atf3) are coloured green (i.e. indicating higher expression in alginate cultures); genes in orange are predicted. Genes more highly expressed in monolayer are not shown (absence of red-coloured genes). In monolayer chondrocytes PDGF BB mediated effects are predicted to be inactive for the observed expression profile, i.e. activated in alginate cultures. Ingenuity® canonical pathways significantly enriched for this expression profile included ‘NRF2-mediated oxidative stress’, ‘PI3K/AKT signalling’ and ‘the role of osteoblasts, osteoclasts and chondrocytes in rheumatoid arthritis’. The physiological function terms ‘differentiation of cells’ (p = 1.6e-14) and ‘apoptosis’ (p = 4.9e-12) were highly enriched in this subnetwork. Nodes with a pink border were enriched for ‘condensation of cartilage tissue’, p = 2.07e-7. The small molecule inhibitor of the PI3K/AKT pathway ‘LY294004’ was predicted to be activated based upon the supplied gene expression profile (z-score = 4.58, overlap p-value = 3.3e-15, 219 gene interactions). This mechanistic network indicates that PI3K signalling and PDGF BB are likely to be active in the redifferentiation phenotype in alginate cultures; the PI3K inhibitor LY294004 describes the inverse for monolayer cells. (b) Using the same elements a protein-protein association network consisting of nodes (proteins) and edges (evidence of associations) indicates a shared function between selected nodes, but not necessarily physical interactions. Sources for associations are defined in the network legend. Elements determined to influence differentiation status of chondrocytes and tenocytes in culture are shown to have significant enrichment for protein-protein interactions (p < 0.0001) indicating that as a group they are biologically connected. Some elements did not demonstrate evidence of association in this network (GPNMB, CHI3L).