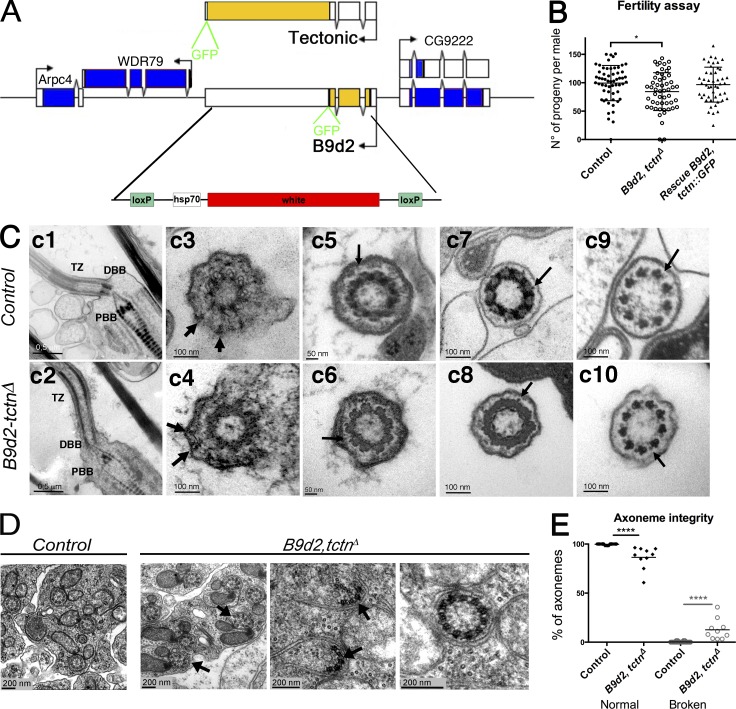
Figure 3.
B9d2, tctn mutant flies show only mild fertility defects. (A) Scheme of the tctn and B9d2 loci. Coding sequences were replaced by the white gene using CRISPR/Cas9-induced homologous recombination. (B) Quantification of the number of progeny obtained from individual males (control n = 58; B9d2, tctnΔ n = 52; and rescue n = 47) mated with three females. Scattered plot representation with mean and SD; *, P < 0.05. (C) Transmission EM analysis of adult antennae chordotonal neurons in control (c1, c3, c5, c7, and c9) or B9d2, tctnΔ mutant flies (c2, c4, c6, c8, and c10). (c1 and c2) Longitudinal sections showing no differences in the organization of the BB and TZ region of the cilia. (c3 and c4) Cross sections at the distal part of the BB show transition fibers connecting the BB to the membrane (arrows) in control and B9d2, tctnΔ mutant flies. (c5 and c6) Cross sections of the proximal part of the TZ. “Y-like” connectors (arrows) are observed in control and B9d2, tctnΔ flies. (c7 and c8) Cross sections of the distal part of the TZ. Small protrusions emanating from the axoneme and directed toward the membrane are observed (arrows) in both control and B9d2, tctnΔ flies. (c9 and c10) Cross sections at the proximal part of the sensory cilia show the ninefold symmetry of doublet microtubules and presence of the dynein arms (arrows) in control and B9d2, tctnΔ flies. DBB, distal basal body; PBB, proximal basal body; TZ, transition zone. (D) Transmission EM observations of adult testis sections. In mutant testis, a few broken (left and center, black arrows) or odd axonemes (11 doublets on the right) are found compared with control. (E) Quantification of the percentage of abnormal axonemes found per normal (n = 20) or mutant (n = 10) cysts. Results are presented as a scattered plot with mean and SD; ****, P < 0.0001.