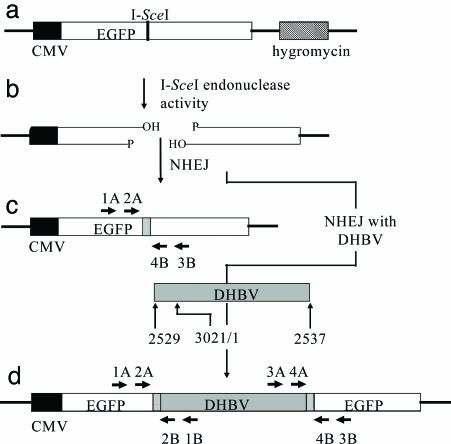
Fig. 1.
Substrate and potential products of NHEJ. (a) Integration target site present in LMH 3.2 cells, consisting of an I-SceI 18-bp recognition sequence inserted into an EGFP gene and the hygromycin-resistance gene for selection. (b) A double-strand break formed by I-SceI endonuclease activity. (c) Product formed by NHEJ of a double-strand break. Precise joining would recreate the I-SceI site, whereas imprecise NHEJ can result in deletions or insertions with concomitant loss of the recognition sequence (gray box). EGFP-specific primer sets 1A/3B and 2A/4B were used to amplify products (see Fig. 2). (d) Product formed by NHEJ, resulting in the integration of DHBV at the double-strand break. The hypothetical DHBV integration substrate shown represents the larger-than-genome size, in situ primed linear DNA, which is the major form of linear DHBV. Integration can be associated with small deletions or insertions of sequence (gray boxes). Left EGFP/DHBV junctions were amplified by nested PCR of genomic DNA by using the primer pairs 1A/1B followed by 2A/2B. Right EGFP/DHBV junctions were amplified similarly from the same genomic DNA by using primers 3A/3B and then 4A/4B.