Fig. 4.
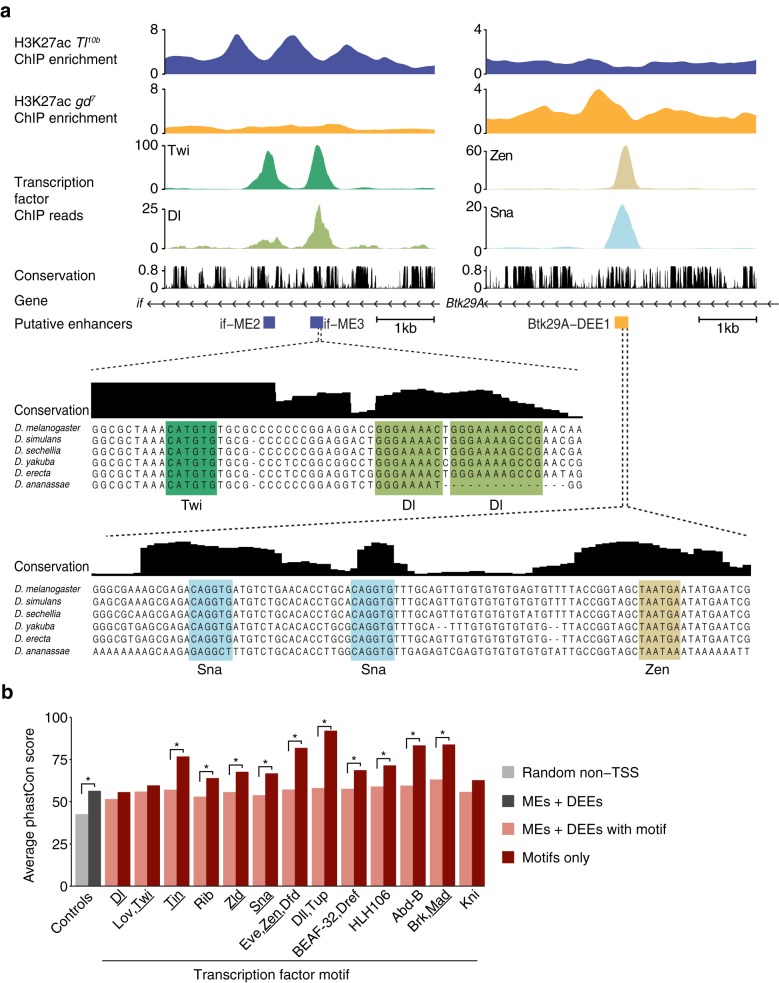
Transcription factor binding motifs are conserved in novel DV enhancers. a Examples of conserved motif instances within a mesoderm enhancer (if-ME3, left), close to the gene inflated (if), and a dorsal ectoderm enhancer (Btk29A-DEE1, right), close to the Btk29A gene. H3K27ac is shown as normalized ChIP enrichment over input in Tl 10b and gd 7 embryos. ChIP-seq occupancy is shown for Twi and Dl (left) and Zen and Sna (right) as ChIP-seq reads normalized to reads per million. A close-up of the if-ME3 sequence shows a canonical Twi binding motif (E-box) and two Dl binding sites that are conserved across several Drosophila species. A close-up of the Btk29A-DEE1 sequence shows two canonical Sna binding motifs and a canonical Zen binding motif that reside in islands of conservation. Conservation data are phastCons data obtained from the UCSC genome browser [72]. b Conservation of all identified DV motifs among all MEs and DEES. The average phastCons score for all putative DV enhancers (”MEs + DEEs” in dark gray) is significantly higher compared to control regions (”Random non-TSS” in light gray). The average phastCons score of each DV motif (”Motifs only” in red) is in many cases higher than that of the surrounding regions (”MEs + DEEs with motif” in light red). This confirms that motifs like that of Zen and Sna are indeed preferentially found in islands of conservation. Significance was determined by Wilcoxon rank-sum test and marked with a star (p < 0.05)