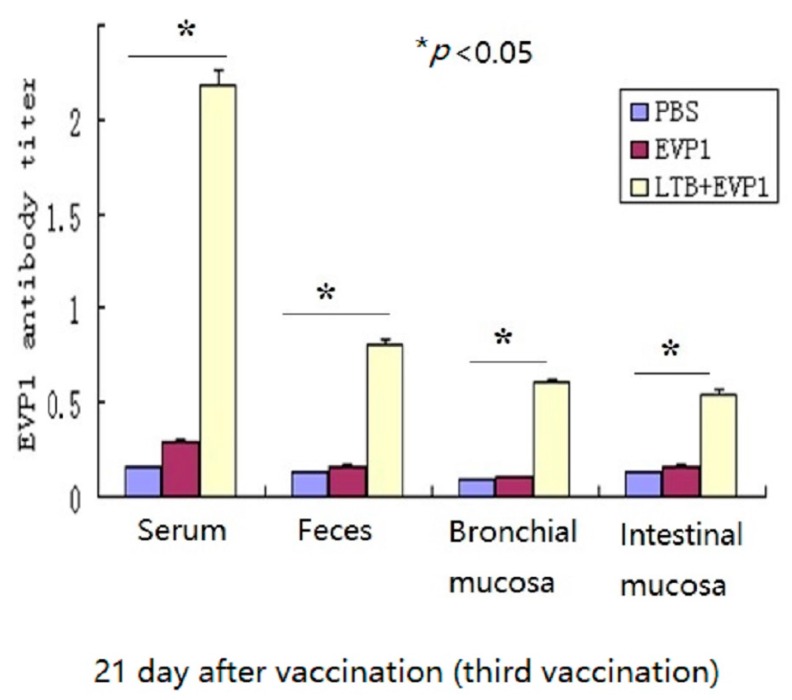
Figure 1.
Labile toxin B subunit (LTB) significantly enhanced the immunogenicity of enterovirus 71 VP1 subunit (EVP1) vaccine. Balb/c mice of 3–4 weeks (male) were divided into four groups (6 mice in each group) as LTB, EVP1, LTB+EVP1, and PBS (phosphate buffer saline). After anesthetizing with chloral hydrate, the mice were vaccinated intranasally three times on day 0, 7, and 14 with 10–20 µL of LTB (10 µg/mL each mouse), EVP1 (10 µg/mL each mouse), LTB + EVP1 (20 µg/mL each mouse), and PBS, respectively. Samples were individually collected from immunized mice on day 21. Endpoint titers were determined as the dilution of each sample from groups of EVP1, LTB+EVP1, and PBS which showed a 2.1-fold higher absorbance level of 450 nm as compared to that of the negative control samples. Average OD450 values for the animals were calculated. The specific antibodies of EVP1 were significantly increased in LTB+EVP1 treatment (* p < 0.05).