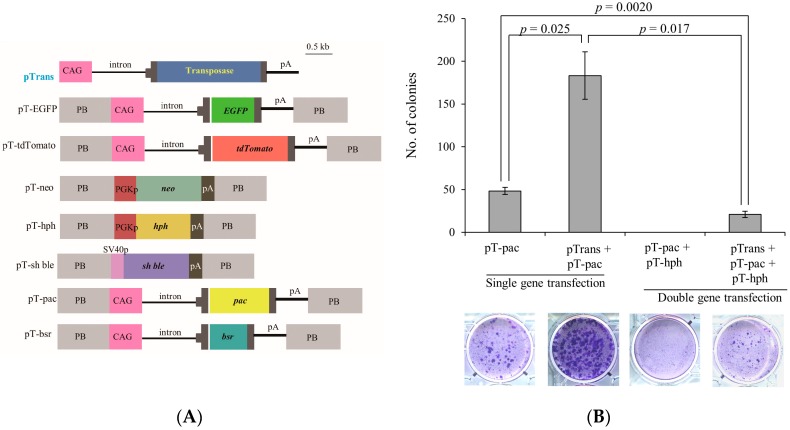
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic representation of selectable marker expression vectors. Plasmid backbone is not shown in this figure. CAG, cytomegalovirus enhancer + chicken β-actin promoter; pA, poly(A) sites; hph, hygromycin phosphotransferase gene; PGKp, mouse phosphoglycerate kinase promoter; neo, neomycin resistance gene; pac, puromycin-N-acetyltransferase gene; bsr, blasticidin S deaminase gene; SV40p, SV40 early promoter; PB, acceptor site in piggyBac system; and Sh ble, a protein that binds to zeocin and prevents it from binding DNA; and (B) beneficial effects of piggyBac-based gene delivery for efficient acquisition of stable transfectants. PEFs were transfected with a single PB vector (pT-pac) in the presence or absence of a transposase expression vector, pTrans (pT-pac vs. pTrans + pT-pac in “single gene transfection”), as described in the Materials and Methods. Similarly, they were transfected with double PB vectors (pT-pac + pT-hph) in the presence or absence of pTrans (pT-pac + pT-hph vs. pTrans + pT-pac + pT-hph in “double gene transfection”). After drug selection, emerging colonies were counted by staining with Giemsa. Photographs taken after Giemsa staining are shown above each column, together with the number of colonies generated.