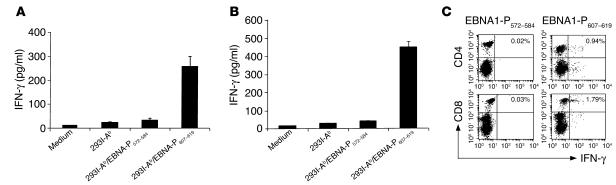
Figure 4.
Characterization of EBNA1-P607–619 peptide–specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. (A) Recognition of EBNA1-P607–619peptide by CD4+ T cells. Mice were immunized with EBNA1P607–619 peptide loaded onto bone marrow cell–derived DCs. After 2 weeks, splenocytes were prepared and stimulated in vitro with the peptide for 6 days, then tested against the same peptide-pulsed 293I-Ab cells for T cell recognition. EBNA1-P572–584 peptide was used as a control. Data are means ± SEM of triplicate cultures. (B) Recognition of peptide-pulsed EL-4 target cells by CD8+ T cells. (C) Intracellular staining of EBNA1 peptide–specific T cell responses. For intracellular IFN-γ staining, splenocytes were stimulated in vitro with EBNA1P607–619 or EBNA1-P572–584 (control) peptide overnight and stained with anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 mAb, respectively, followed by intracellular IFN-γ staining. The double-positive T cells were identified by FACS analysis. The percentage of double-positive cells is given in the upper right of each panel.