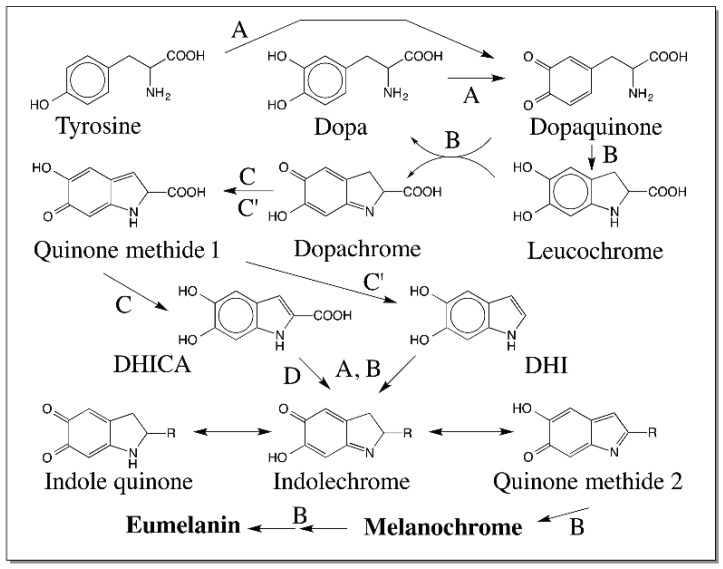
Figure 27.
Modified Raper–Mason Pathway for eumelanin biosynthesis. Tyrosinase (A) converts tyrosine to dopaquinone and oxidizes dopa to dopaquinone. External addition of cysteine to dopaquinone and the oxidative polymerization of cysteinyldopa result in the production of pheomelanin pigments (not shown in Figure). Intramolecular cyclization of dopaquinone produces leucochrome, which is further oxidized to dopachrome by nonenzymatic reactions (B). Dopachrome is isomerized to transient quinone methide (1) that is converted to either DHICA by mammalian DCT (C) or DHI by insect DCDT (C′). Oxidation of these two indoles by tyrosinase or nonenzymatic reactions or by DHICA oxidase (D) produces among other reactive species, quinone methides, which will have a major role in eventual polymerization of these monomeric compounds (R = H for DHI derivative; and COOH for DHICA derivative).