Fig. 1.
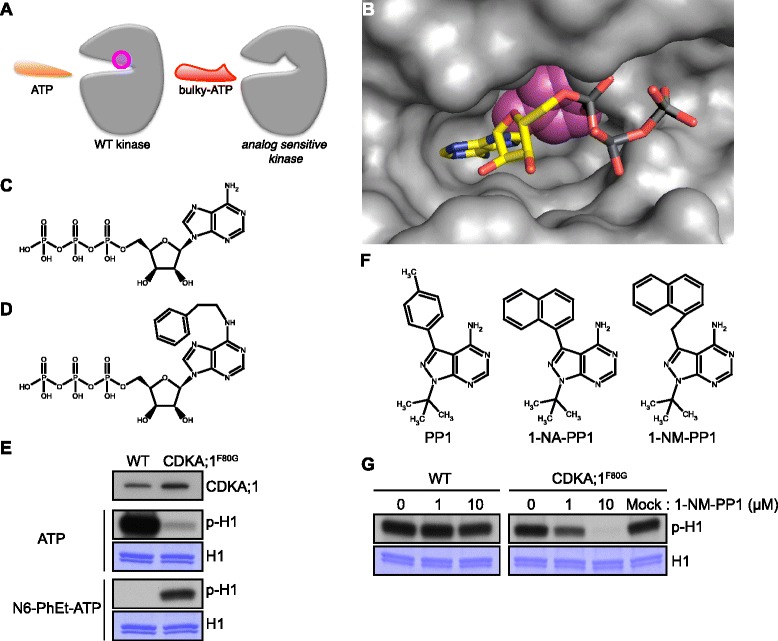
Generation and characterization of an analog-sensitive variant of CDKA;1. a Sketch of an analog-sensitive kinase variant (right) that has an enlarged ATP-binding pocket in comparison with the wild-type version (left) through exchanging a ‘gatekeeper’ amino acid (position in magenta), typically a large amino acid, in the wild-type version with a small one such as Gly. An analog-sensitive kinase can use regular ATP but also bulky derivatives that cannot be used by the wild-type variant as a phosphate donor (see also below). b Computed 3D structure of the ATP binding pocket of CDKA;1. In magenta, the space occupied at the bottom of the pocket by the gatekeeper amino acid Phenylalanine (Phe/F) 80 in the wild-type kinase that will be enlarged by the F80 to Glycine (Gly/G) mutation. c Structure of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). d Structure of the bulky-ATP derivate N6-(2-Phenylethyl)adenosine-5′-O-triphosphate (N6-PhEt-ATP). e In vitro kinase assay with wild-type and the analog-sensitive CDKA;1 (CDKA;1F80G) kinases using CYCD3;1 as a cyclin partner and histone H1 as a generic substrate. First lane from the top, protein blotting reveals equal amounts of CDKA;1 proteins in the reaction. Second lane, kinase assays with [γ-32P]-ATP as a phosphate donor. Forth lane, kinase assays with [γ-32P]-N6-PhEt-ATP as a phosphate donor. Proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE after the kinase reaction and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 demonstrating equal loading of the substrate, lane three and five from the top. Abbreviations: p-H1 for radio-labeled histone H1 resulting from kinase assays with radio-labeled ATP, H1 for histone H1. f Structure of the broad band kinase inhibitor 4-amino-1-tert-butyl-3-phenylpyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine (PP1) on the left and the bulky analogs 4-amino-1-tert-butyl-3-(1′-naphthyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine (1-NA-PP1) in the middle as well as 4-amino-1-tert-butyl-3-(1′-naphthylmethyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine (1-NM-PP1) on the right. g In vitro kinase assay with wild-type and the analog-sensitive CDKA;1 (CDKA;1F80G) kinases using CYCD3;1 as a cyclin partner and histone H1 as a generic substrate. Inhibition of wild-type (left) and the analog-sensitive CDKA;1 (right) kinases with 0, 1, and 10 μM of the PP1 derivative 1-NM-PP1. Proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE after the kinase reaction with [γ-32P]-ATP as a phosphate donor and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 demonstrating equal loading of the substrate. Mock was treated with 0.1 % (v/v) DMSO, the solvent of 1-NM-PP1. Abbreviations: p-H1 for radio-labeled histone H1 resulting from kinase assays with radio-labeled ATP, H1 for histone H1. Chemical structures in this figure were drawn with MarvinSketch, version 5.0.02 (ChemAxon, Hungary)
