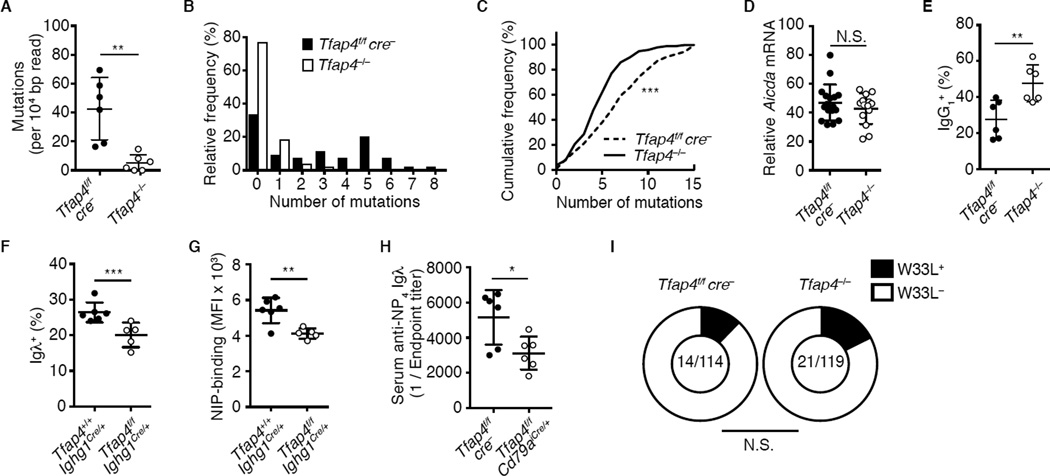
Figure 5. AP4 is necessary for the accumulation of somatic mutations.
(A) Frequencies of mutations in an JH4 adjacent intronic region in Tfap4−/− and control Tfap4f/fcre− donor GC B cells from mixed bone marrow chimeras 12 days after NP-CGG immunization. Data are pooled from three independent experiments.
(B) Frequencies of clones carrying multiple mutations in (A).
(C) Cumulative frequency distribution of VH186.2 somatic mutations in CD45.2 donor GC B cells in (A). Data are pooled from three independent experiments.
(D and E) Expression of Aicda mRNA and frequencies of IgG1+ in CD45.2 donor-derived GC B cells in (A). Data are pooled from three independent experiments.
(F) Frequencies of Igλ+ cells in NIP-APC-binding GC B cells from Tfap4f/fIghg1cre/+ and control Tfap4+/+Ighg1cre/+ mice ten days after NP-CGG immunization. Data are pooled from two independent experiments.
(G) NIP-APC-binding by GC B cells in (F). Data are pooled from two independent experiments. (H) NP4-specific serum Igλ titers in Tfap4f/fCd79aicre/+ and control Tfap4f/fcre− mice 56 days after NP-CGG immunization. Data are pooled from two independent experiments.
(I) Frequencies of the W33L mutation in VH186.2 BCR+ clones in CD45.2 GC B cells in (A). Numbers of W33L bearing clones and total number of clones sequenced are shown. Data are pooled from four independent experiments.
Data in (A, D, E, F-H) are shown by means ± SD, with unpaired Student’s t test. Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for (C). c2 test with Yates correction for (I). n = 6 for each group (A-C, E-I); n = 17 for Tfap4f/fcre− and n = 14 for Tfap4−/− (D). See also Figure S5.