FIG 1.
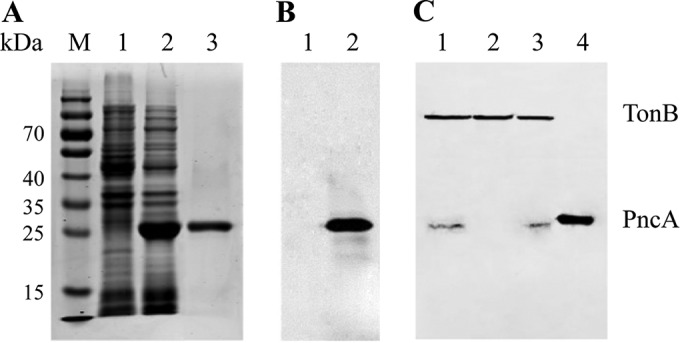
Expression and identification of R. anatipestifer PncA. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of rPncA. Lane M, molecular weight markers; lane 1, negative control, i.e., E. coli BL21(DE3) transformed with pET-28a(+), with IPTG induction; lane 2, supernatant from E. coli BL21(DE3) transformed with pET-pncA, with IPTG induction; lane 3, purified rPncA. (B) Western blot profile. Lane 1, negative control, i.e., E. coli BL21(DE3) transformed with pET-28a(+), with IPTG induction; lane 2, E. coli BL21(DE3) transformed with pET-pncA, with IPTG induction. (C) Identification of the complemented strain cYb2ΔpncA by Western blot analysis. A second antibody against the TonB-dependent receptor of R. anatipestifer was used to control for protein loading. Lane 1, whole-cell proteins from the wild-type strain Yb2; lane 2, whole-cell proteins from the mutant strain Yb2ΔpncA; lane 3, whole-cell proteins from the complemented strain cYb2ΔpncA; lane 4, positive control, i.e., supernatant from E. coli BL21(DE3) transformed with pET-pncA, with IPTG induction.
