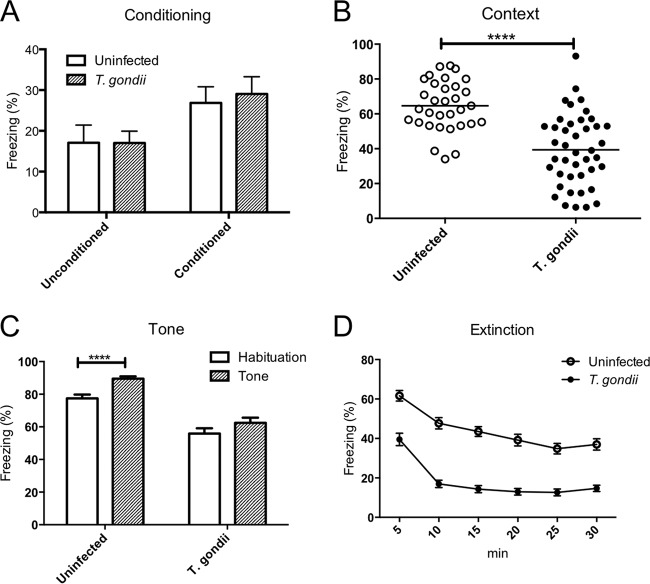
FIG 1.
Impaired long-term fear memory consolidation in uninfected and T. gondii-infected mice. The ordinate shows the percentage of time spent freezing. (A) The unconditioned trial shows freezing during the first tone before pairing to foot shock, and the conditioned trial shows freezing during the second tone after pairing to foot shock on test day 1. (B) Contextual conditioned freezing time. (C) Tone-conditioned freezing time. (D) Extinction of tone-conditioned freezing time. Significant differences were determined by unpaired t tests (****, P < 0.0001) (A to C) and a repeated-measures ANOVA with the post hoc Bonferroni test (D). Significant main effects were shown for T. gondii infection [F(1, 70) = 75.90, P < 0.0001] and time [F(5, 350) = 117.5, P < 0.0001], and their interaction was also significant [F(5, 350) = 4.410, P < 0.001]. Freezing was calculated by dividing freezing time into the times for observation (300 s) in the context test, habituation (180 s), tone (180 s) during the tone test, and 5 min for every 5 min in the extinction test. Data represent means ± SEMs. Data are for uninfected mice (n = 32) and T. gondii-infected mice (n = 42) and are summarized from four independent experiments.