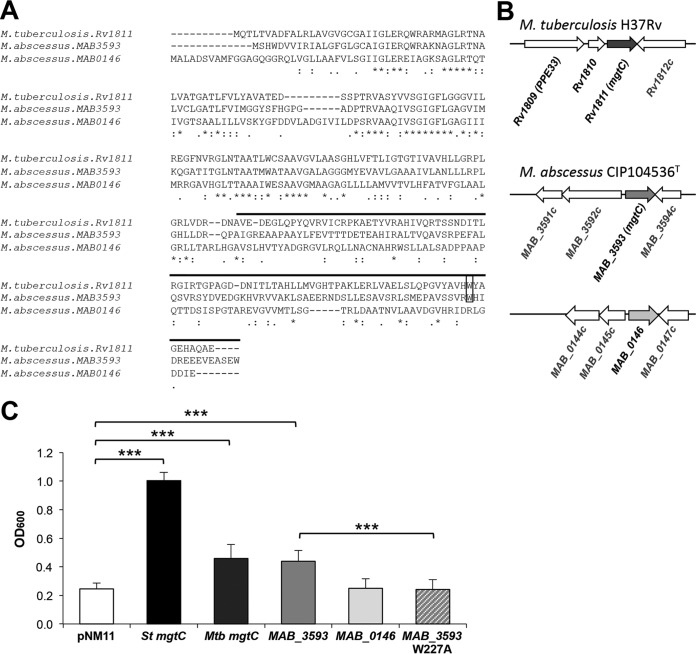
FIG 1.
MgtC-like proteins encoded by M. abscessus genome. (A) Alignment of M. tuberculosis MgtC (MgtCMTB) and M. abscessus MgtC-like proteins (MAB_3593 and MAB_0146) was done with the T-COFFEE Multiple Sequence Alignment Server (tcoffee.crg.cat/). The upper line indicates the predicted soluble C-terminal part. Near the C terminus, a conserved tryptophan residue identified as important for MgtC function in Salmonella in Mg2+-deprived medium is indicated by a black rectangle. Conservation of residues is indicated below the sequences as follows: asterisk (*), residues that are identical in all sequences in the alignment; colon (:), conserved substitutions; period (.), semiconserved. (B) Genomic organization around mgtC-like genes. (C) Functional analysis of M. abscessus MgtC-like proteins by heterologous complementation of a Salmonella mgtC mutant strain compared to MgtCMTB. A Salmonella Typhimurium (St) mgtC mutant was transformed with plasmids harboring MAB_3593, MAB_0146, or mgtCMTB (Rv1811). A mutation was introduced in MAB_3593 to test the role of functional relevance of the W227 residue. The OD600 was measured after growth of complemented strains in medium with a low concentration of Mg2+ for 18 h. A negative control was provided with a strain harboring an empty vector (pNM11), whereas a positive control was provided with a strain expressing the Salmonella mgtC gene (mgtCST). Data represent the mean values plus standard errors of results from at least three independent experiments. Mtb, M. tuberculosis; ***, P < 0.001 (Student t test).