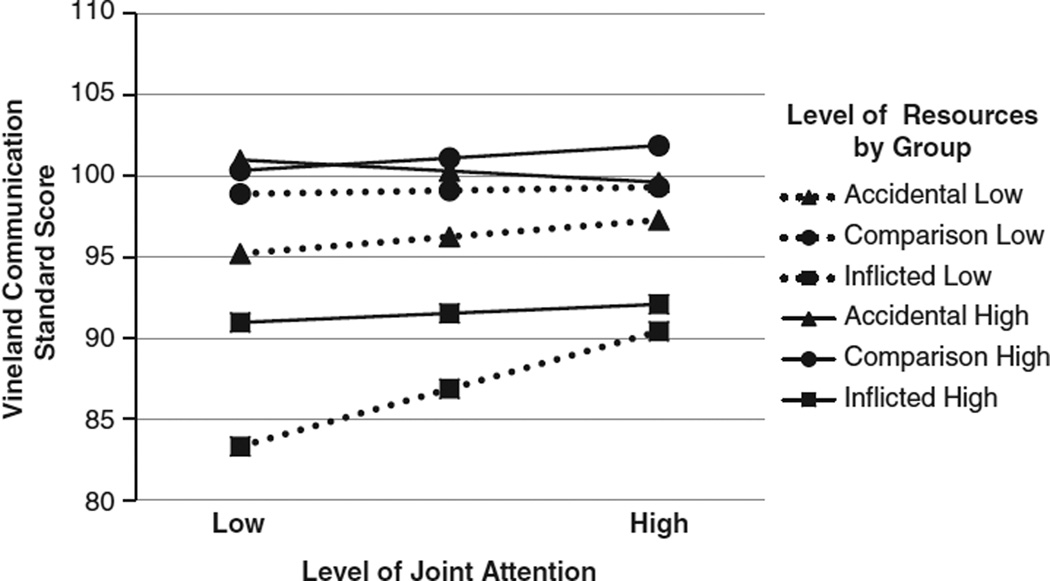
Fig. 4.
Family resources tended to interact with the level of joint attention to influence Vineland Communication scores. For children with inflicted traumatic brain injury (TBI), higher family resources had a protective effect and lower resources had a detrimental effect on everyday communication in children with lower responsiveness in social interactions.