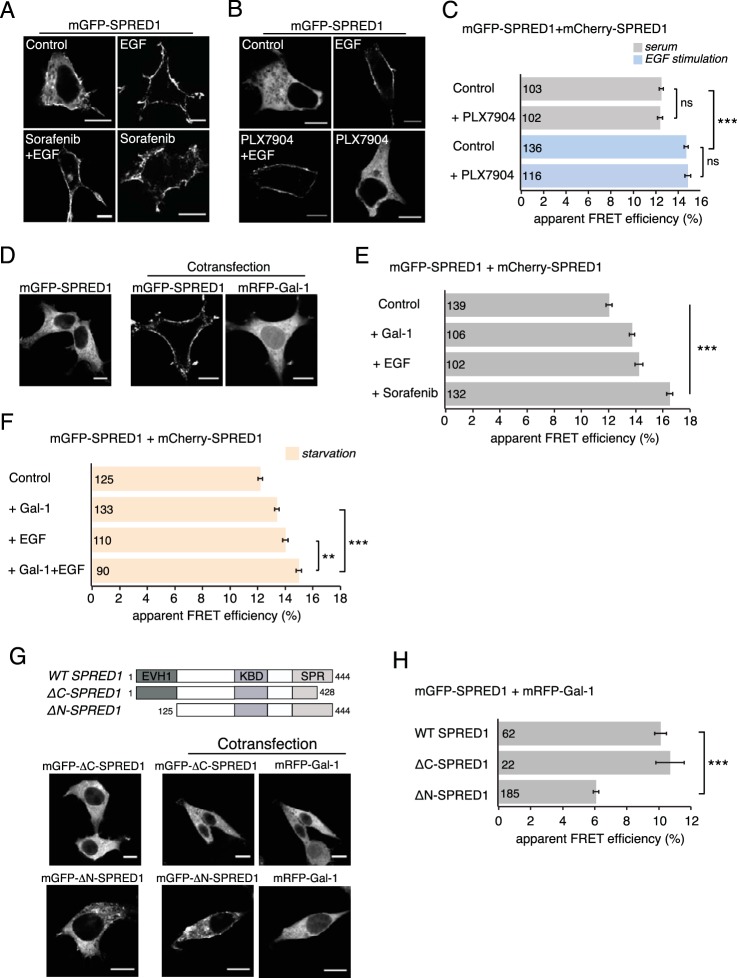
FIG 1.
Raf inhibitor sorafenib or galectin-1 induces SPRED1 plasma membrane translocation. (A) Confocal images of HEK cells transiently transfected with mGFP-SPRED1 for 24 h, followed by control treatment (0.5% DMSO in growth medium) for 2 h, serum starvation for 5 h and stimulation with EGF (100 ng/ml, 10 min), serum starvation for 5 h and sorafenib treatment (50 μM, 2 h) followed by EGF stimulation (100 ng/ml, 10 min), or sorafenib treatment alone (50 μM, 2 h), as indicated. Scale bars, 10 μm. (B) HEK cells were transiently transfected with mGFP-SPRED1 for 24 h, followed by control treatment (0.1% DMSO in growth medium) for 1 h, serum starvation for 5 h and stimulation with EGF (100 ng/ml, 10 min), serum starvation for 5 h and PLX7904 treatment (10 μM, 1 h) followed by EGF stimulation (100 ng/ml, 10 min), or PLX7904 treatment alone (10 μM, 1 h), as indicated. The cells were imaged by confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 10 μm. (C) A SPRED1 membrane translocation FRET assay was conducted in HEK cells transiently coexpressing mGFP-/mCherry-SPRED1. After 24 h of transfection, the cells were treated as described for panel B and fixed. Numbers inside the bars correspond to the total number of cells studied in each case. Error bars indicate the standard errors of the means. ***, P < 0.001; ns, nonsignificant. (D) mGFP-SPRED1 and mRFP–Gal-1 were transiently cotransfected in HEK cells for 24 h and imaged by confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 10 μm. (E) A SPRED1 membrane translocation FRET assay was conducted in HEK cells transiently coexpressing mGFP-/mCherry-SPRED1. The cells were coexpressed with untagged Gal-1 or starved for 5 h and stimulated with EGF (100 ng/ml, 10 min) or treated with sorafenib (50 μM, 2 h). Numbers inside the bars correspond to the total number of cells studied in each case. Error bars indicate the standard errors of the means. ***, P < 0.001. (F) A SPRED1 membrane translocation FRET assay was conducted in HEK cells transiently coexpressing mGFP-/mCherry-SPRED1. The cells were starved for 5 h (control) or coexpressed with untagged Gal-1 and starved for 5 h, or starved for 5 h and stimulated with EGF (100 ng/ml, 10 min), or coexpressed with untagged Gal-1 followed by starvation for 5 h and stimulation with EGF (100 ng/ml, 10 min). Numbers inside the bars correspond to the total number of cells studied in each case. Error bars indicate the standard errors of the means. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. (G) mGFP-ΔC-SPRED1, a C-terminal deletion mutant, or mGFP-ΔN-SPRED1, an N-terminal deletion mutant, was cotransfected together with mRFP–Gal-1 for 24 h in HEK cells and imaged by confocal microscopy, as indicated. The schematic representation of domain structures shows the differences between wild-type (WT) SPRED1 and the deletion mutants. The ΔC-SPRED1 mutant lacks 26 amino acids from the C terminus, and the ΔN-SPRED1 mutant lacks 124 amino acids from the N terminus. EVH1, Ena/vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) homology-1 domain; KBD, c-Kit-binding domain; SPR, Sprouty-related domain. Scale bars, 10 μm. (H) Interaction between WT mGFP-SPRED1 or mGFP-tagged SPRED1 mutants with mRFP–Gal-1 was detected using FRET in HEK cells transiently expressing the constructs as indicated. Numbers inside the bars correspond to the total number of cells studied in each case. Error bars indicate the standard errors of the means. ***, P < 0.001.