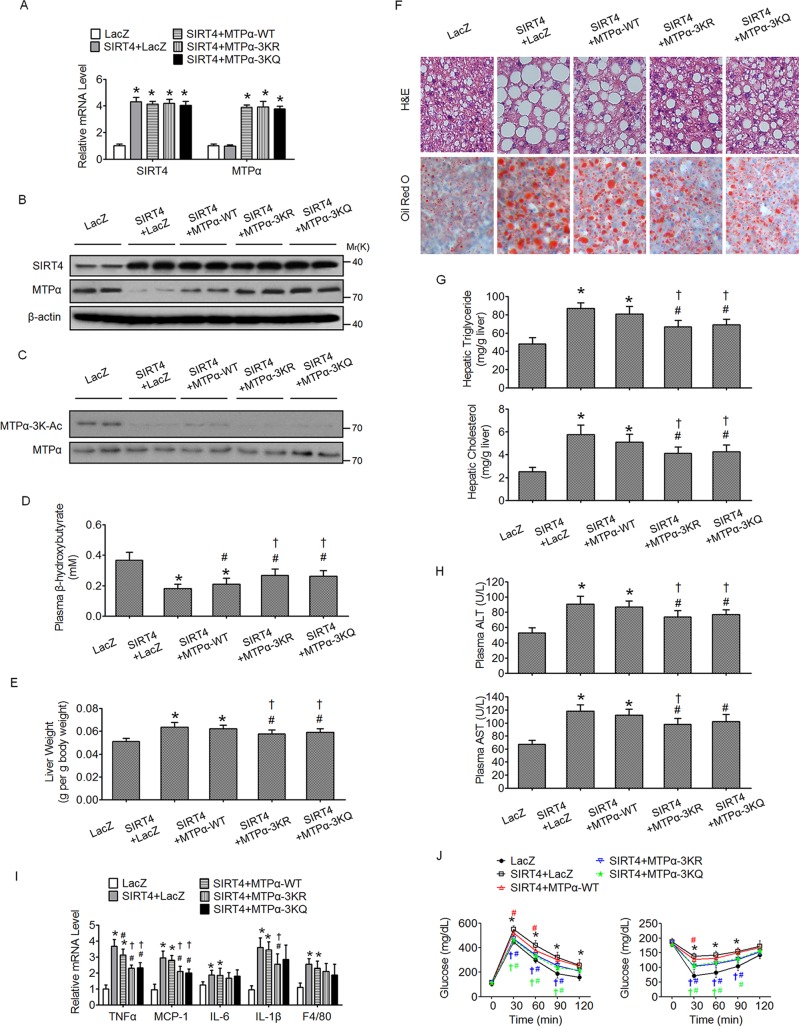
FIG 8.
Deacetylation of MTPα by SIRT4 contributes to SIRT4-mediated hepatic steatosis in HF/HS diet-fed mice. (A and B) Male C57BL/6J mice fed an HF/HS diet for 2 months were injected once a week with adenovirus encoding SIRT4, together with or without adenovirus encoding WT MTPα or 3K mutant MTPα, through the tail vein. Measurements were performed at 15 days postinfection. The mRNA levels and protein levels of SIRT4 and MTPα in the livers were determined by RT-qPCR (A) and Western blotting (B). (C) MTPα-3K acetylation levels were compared to MTPα protein levels. (D) Plasma β-hydroxybutyrate levels. (E) Organ weights. (F) Representative images of H&E staining and Oil Red O staining of liver sections (magnification, ×100). (G) Triglyceride and cholesterol levels in livers. (H) Levels of plasma AST and ALT. (I) Expression levels of inflammatory genes in livers. (J) GTT (left) and ITT (right) results. *, P < 0.05 versus LacZ; #, P < 0.05 versus SIRT4 plus LacZ; †, P < 0.05 versus SIRT4 plus MTPα-WT. n = 6 to 10/group. The error bars indicate SD.