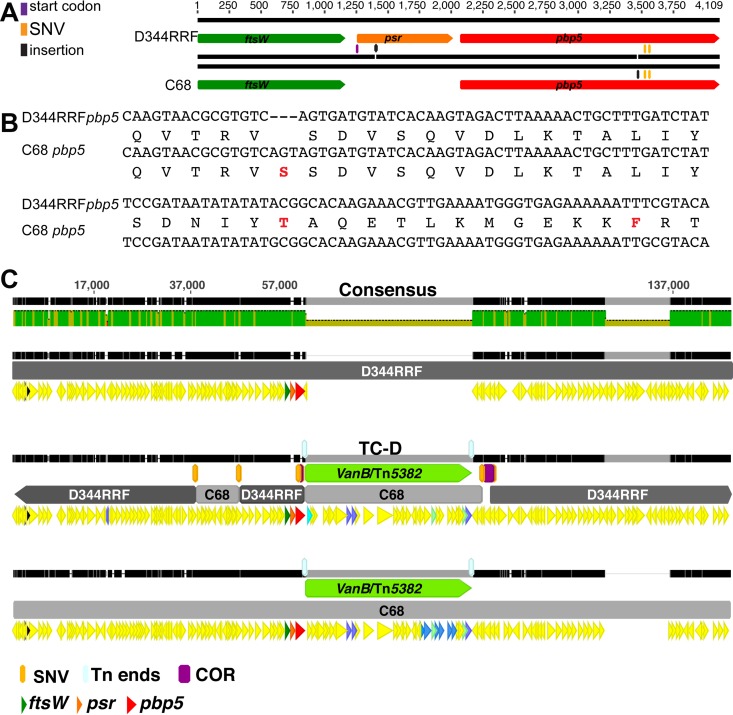
FIG 2.
pbp5 and TC-D insertion site. (A) pbp5 operon cartoon showing the differences between strains D344RRF and C68. In C68, an insertion (C) 153 bp downstream of the ribosomal binding site causes a frameshift introducing a premature stop codon 309 bp downstream of the start of the gene, possibly generating a nonfunctional gene. (B) The sequence of the pbp5 gene in C68 codes for an extra serine and has two amino acid substitutions compared with the sequence of D344RRF (red). (C) Alignment of D344RRF, TC-D, and C68 in the region of integration of Tn5382 carrying vanB. Green, the vancomycin resistance-carrying transposon; light blue, the transposon (Tn) ends flanking the vancomycin resistance-carrying transposon; light gray, the segments in which the C68 genome replaced that of D344RRF in the transconjugant; purple, the crossover regions (COR) flanked by the SNV used to identify the region. Note the additional C68 integration in TC-D upstream of the pbp5 operon. pbp5 from D344RRF was not replaced by that of C68 in this transconjugant. SNV, single nucleotide variant.