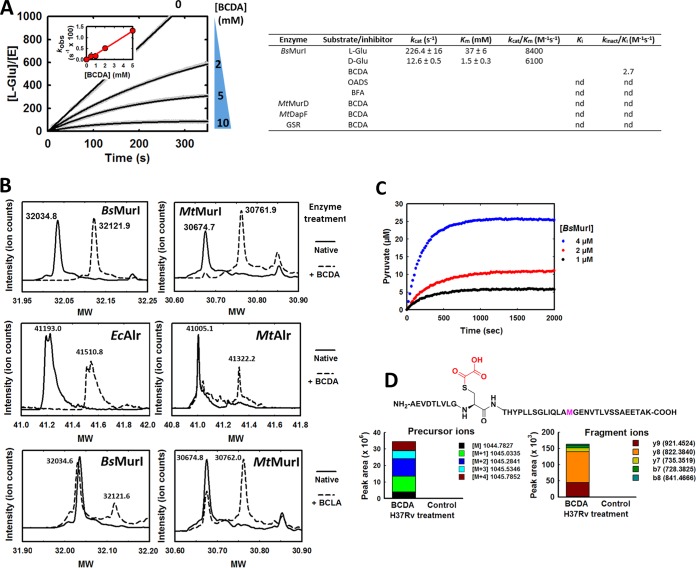
FIG 4.
BCDA is an irreversible-mechanism-based inhibitor of glutamate racemase. (A) Time-dependent inhibition kinetics of BCDA against recombinant BsMurI. Time courses displayed are representative of results of at least triplicate independent assays. The inset shows a replotting of kobs versus BCDA concentration. Values in the table represent derived kinetic parameters for enzymes mentioned in this study (nd, not detected). GSR, S. cerevisiae glutathione reductase; BFA, β-fluoro-alanine (racemic mix); OADS, O-acetyl–d-serine. Data shown are the averages ± SEM of at least triplicate data sets. (B) ESI-MS analysis of intact molecular weights (MW) of untreated (solid lines) and BC(d/l)A-treated (dashed lines; 10 mM for 1 to 2 h, 37°C) recombinant BsMurI and MtMurI (top and bottom panels) and EcAlr and MtAlr (middle panels). (C) BCDA inhibition of BsMurI proceeds via a 2-AA intermediate. Pyruvate production by BsMurI in the presence of BCDA was measured using a coupled enzyme (pyruvate kinase/lactic dehydrogenase [PK/LDH]) assay. The BCDA concentration was held constant at 5 mM. Data displayed are representative of time courses selected from replicate data sets. (D) Local amino acid sequence corresponding to the predominant site of BCDA covalent modification in MtMurI (top) and identification of the BCDA-modified MtMurI peptide in whole-cell lysates derived from BCDA-treated (2× MIC, 24 h) H37Rv cultures, but not untreated control cultures, by LC-MS (bottom). The precursor ions (left panel) refer to the quadruple charge state (+4) of the parent peptide; the right panel displays the fragment ions derived from this precursor ion. Fragments were continuously monitored and were absent from the control sample. See also Fig. S5 and S6 in the supplemental material.