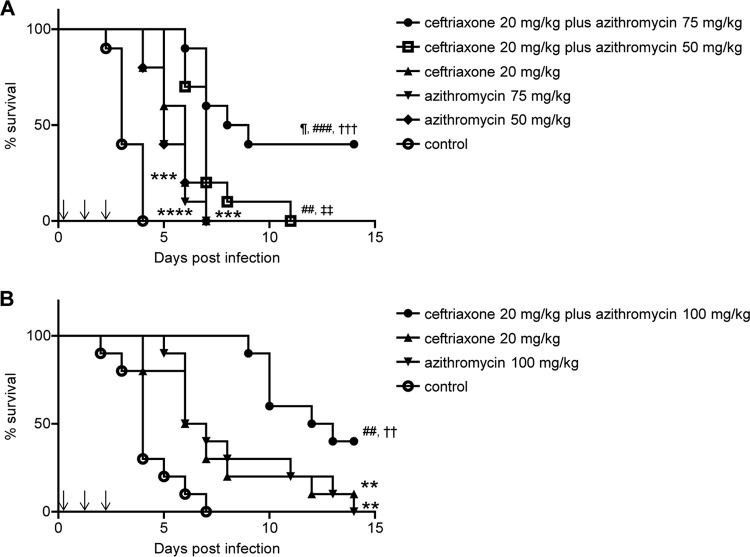
FIG 1.
Effects of ceftriaxone-plus-azithromycin combination therapy on the survival of mice with pneumococcal pneumonia. Treatments (down arrows) were applied three times every 24 h beginning at 6 h after infection. Mouse survival was evaluated every 24 h for a total of 14 days after infection. (A) Mice infected by S. pneumoniae strain 741 were divided into six treatment groups (n = 10 each). The results are displayed as Kaplan-Meier curves and were compared using log-rank tests. ¶, P < 0.05 compared with the ceftriaxone 20 mg/kg plus azithromycin 50 mg/kg combination group; ###, P < 0.001 compared with the ceftriaxone 20 mg/kg group; ##, P < 0.01 compared with the ceftriaxone 20 mg/kg group; †††, P < 0.001 compared with the azithromycin 75 mg/kg group; ‡‡, P < 0.01 compared with the azithromycin 50 mg/kg group; ***, P < 0.001 compared with the control group; ****, P < 0.0001 compared with the control group. (B) Mice infected by S. pneumoniae strain 741 were divided into four treatment groups (n = 10 each). ##, P < 0.01 compared with the ceftriaxone 20 mg/kg group; ††, P < 0.01 compared with the azithromycin 100 mg/kg group; **, P < 0.01 compared with the control group.