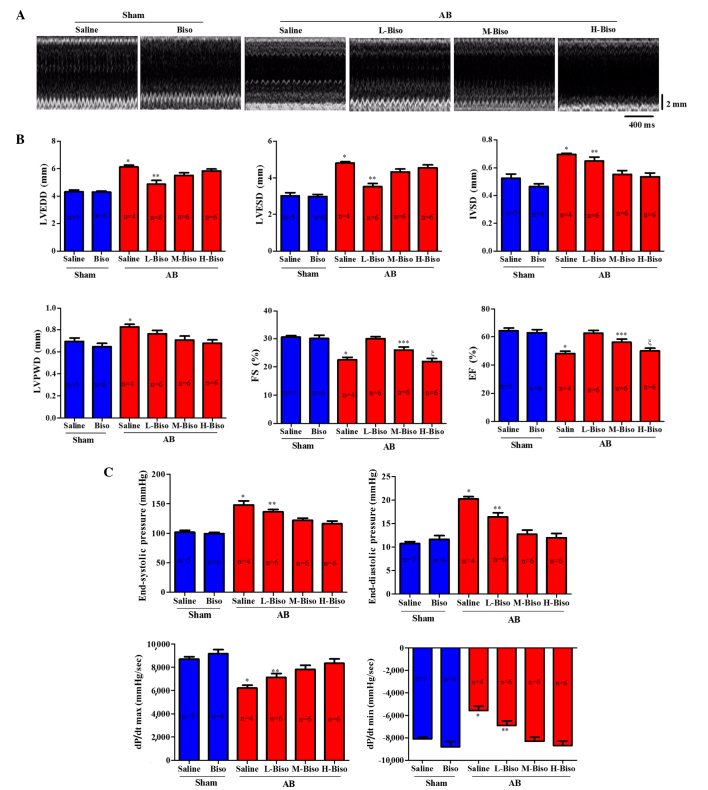
Figure 2.
Bisoprolol increases adverse pressure overload-induced ventricular remodeling. (A) Representative serial M-mode echocardiography in conscious mice from the six experimental groups at 8 weeks after sham or AB surgery. (B) Quantitative analysis of echocardiographic parameters. (C) Summary of hemodynamic data on systolic function and diastolic function. All values are the mean ± standard error of the mean (n=4–6 per group). *P<0.05 vs. all other groups, **P<0.05 vs. M-Biso AB and H-Biso AB, ***P<0.05 vs. H-Biso AB, ξP<0.05 vs. L-Biso AB and M-Biso AB. AB, aortic banding; Biso, bisoprolol; L, low-dose; M, middle-dose; H, high-dose; LVEDD, left ventricular end-diastolic diameter; LVESD, left-ventricular end-systolic diameter; IVSD, left ventricular septum diastolic; LVPWD, left ventricular posterior wall diameter; FS, fractional shortening; EF, ejection fraction; dp/dt, left ventricular contractility.