Figure 4.
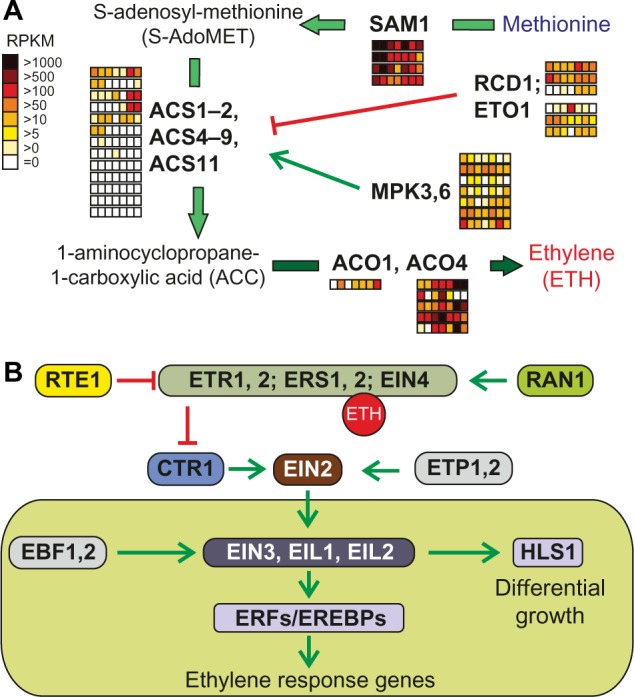
Pathways of ethylene synthesis and signaling. (A) Enzymes and intermediate products of the ethylene production unify to methionine (blue) as precursor for ethylene (red) synthesis. The enzymatic step catalyzed by ACS is inhibited by the action of RCD1 and ETO1 or activated by MPK3 and MPK6. Further details are presented in the text. The arrows are colored according to the species in which the enzymes were found (Fig. 1A). Expression of the identified genes in tomato is shown as explained in Figure 2. (B) The components involved in ethylene signaling are represented as interaction scheme, at which activation of downstream components is indicated by green arrows and inhibition by red bar-headed lines.
Abbreviations: Proteins: SAM, S-adenosylmethionine synthetase; ACS, ACC synthase; RCD, radical-induced cell death; ETO, ethylene overproducer; MPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; ACO, ACC oxidase; ETR/ERS, ethylene response; EIN, ethylene-insensitive; RAN, RAS-related nuclear protein; RTE, reversion-to-ethylene sensitivity; CTR, constitutive triple response; EDR, enhanced disease resistance; EIN, ethylene-insensitive; ETP, EIN2 targeting protein; EIL, ethylene-insensitive 3-like; EBF, EIN3-binding F-box protein; HLS, HOOKLESS.
